アルファロメオ147GTAの予防整備
2016年06月27日
こちらのGTAも、いつもお世話になっております。
今回は147GTAの予防整備ということで暑い夏が来る前に部品を交換しておきましょう!
ということで
交換したのがこちら(^^)/
ASSO 低抵抗オルタネーター(ブラックオルタネーター)!!
カタチは純正そのものかなと思いましたが
並べると意外と違いました(^^;
(並べた写真はありませんが。。。)
プーリーはアルミのビレットが美しいです!!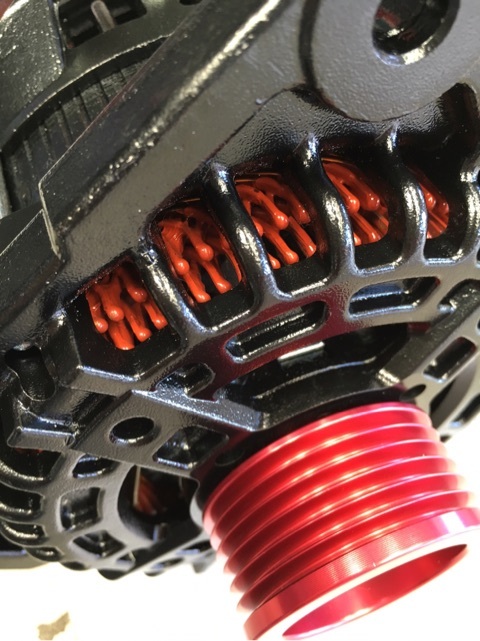
この中の巻き線がポイントですかね??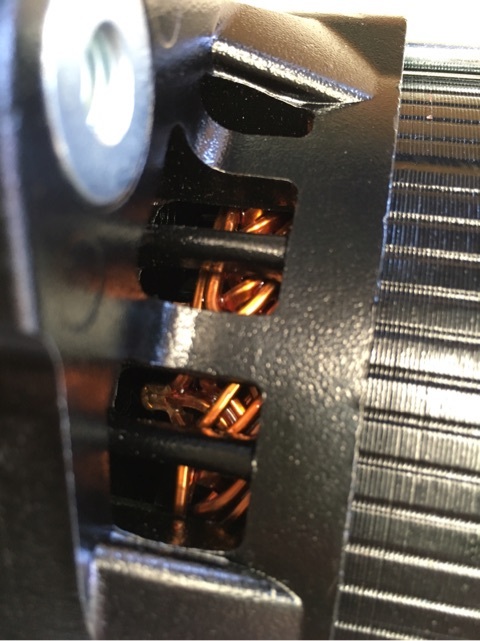
交換には足まわり、ドライブシャフト外して
エンジンはハンガーで宙吊りのサブフレーム脱着の毎度ながらの作業となります。。。
最近アルファロメオの整備を何するにしてもサブフレーム脱着してる気がします(^^;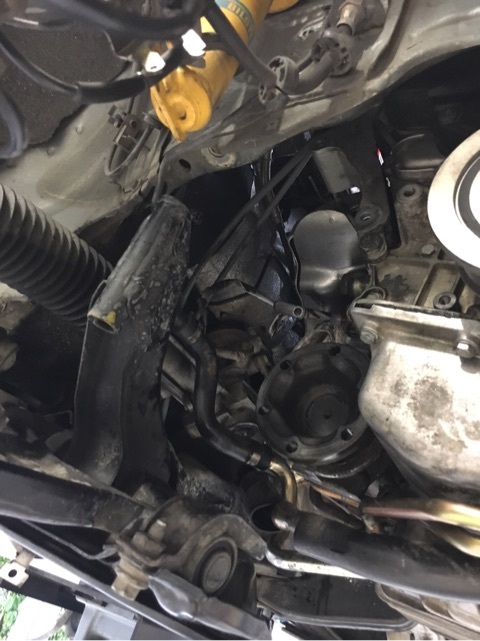
こちらが組み込んだ状態♪
さらにドライブベルトを掛けた状態!
この後サイドカバーを付ければせっかくのカッコいいプーリーが
全く見えなくなってしまいます(T_T)
今回サブフレーム脱着で一カ所サブフレームを固定するメス側のねじ山が
もうダメになってましたのでねじ山修理しました。
ダメなねじ山をドリルで切削後、オーバーサイズのねじ山を切削
その後オーバーサイズのねじ山に元のサイズのねじ山(タマ)を入れ込み。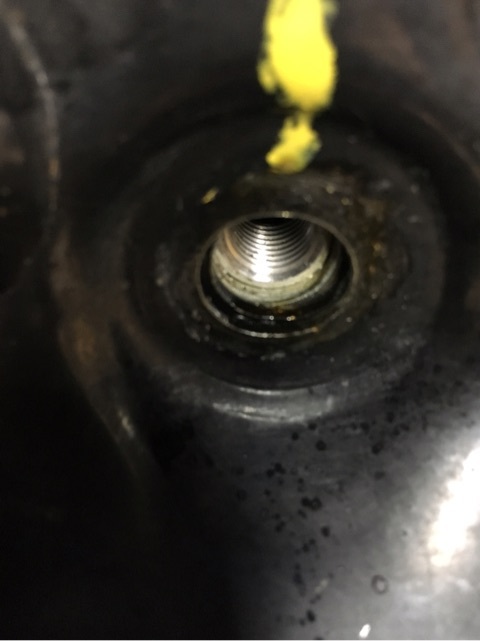
これで元のサイズのボルトで固定が出来るようになるのです(^^)
しかも丈夫!!
さらに今回はサブフレーム脱着した際にフロントパイプも取り外しましたので
組付けの際はこちらを取付!!
ユニコルセ 等長フロントパイプ!!
定番メニューになっておりますが、こちらは受注生産ですので
入荷するまで1ヵ月程はかかります。。。
以上全て組付ければ試乗して点検、細かい調整して完了です!
御入庫ありがとうございました!!
サービス 向島
この記事へのコメント
The VIP program offers real cashback instead of empty points, and 100 free spins on popular games make it a
great entry point for newer players. This list is
only for the real money casinos that actually
deliver in Australia. We’ve played, tested, and cashed out ? not all
online casinos make the cut. In 2025, with so
many online platforms vying for your attention, pinpointing the safest, most reputable, and truly rewarding real money casinos
in Australia can feel overwhelming. Over 30 live casino games are available, too,
with limits suitable for both casual players and high rollers.
This means you can explore a wide variety of gaming opportunities from around
the globe! Enjoy your gaming journey, and may your experience be thrilling
and rewarding! Seeking help provides the necessary guidance and assistance to address gambling issues and promote
responsible practices.
To learn more about how to request a withdrawal
via your online casino account, click?here.
Next, you’ll need to make a deposit; after
all, you’ll need money to play with. For example, many Ignition pokies offer bonus buys; these allow you to buy into a
bonus round instead of having to activate it organically.
First, you’ll find some of the most innovative and lucrative features available today in Ignition’s casino games.
CasinoMentor's database every day, so you never run out of space to satisfy your gambling passion. House of Fun delivers a bold,
colorful social casino experience with hundreds of high-quality slot games and
no real-money wagering required. The casino games at
Slotomania are developed by Playtika, a leading gaming software company, ensuring a top-notch gaming experience for New York players.
Currently, the only way to play real money casino games in New York is to visit one of the
many brick-and-mortar casinos in the state. A new Australian online casino we'd happily add to our list
offers smooth banking that players can trust.
Just check their website to see if it's available for your device.
The complete experience is there, just optimised for touchscreens.
You'll also get cutting-edge software and high game quality
? all wrapped in sleek, up-to-date design. Others team up with well-known game studios to produce site-only releases.
Before you make a real money deposit, we suggest
that you test the availability and responsiveness of the casino’s customer support.
Be mindful that these casinos bonuses come with wagering requirements attached so always read
the terms and conditions before you opt in.
These bonuses usually include a deposit match and free spins that you can use to win real cash.
Once you’ve created an account, you can take advantage of the lucrative welcome or sign-up bonuses offered by the casino.
This involves verifying the identity of players to prevent fraud, money laundering, and underage gambling.
to our endpoint. Once you have signed up
and verified your account, you will need to take note of your SerpApi
API key found on your dashboard so that you can use it in the following steps.
In this blog post, I'm going to describe the basic changes you will need to make to make the move
to SerpApi's Bing Search API. The official Bing
Search API is soon to be retired on 11th August 2025 (or has
already been retired depending on when you're reading this) and you
may be searching for a suitable replacement.
Rafly is a reporter with years of journalistic experience, ranging from technology, business, social,
and culture.
If the issue is not something we can help you with,
call Sky by dialling 150 (free) from either a Sky Talk landline or a Sky mobile.
If you fail to respond to a chat reply within 48 hours the chat
will again close down automatically even if your issue hasn’t been resolved.
I have returned my old sky router following an upgrade to fibre but have
received another text asking me to return it! @Emeka2? Sky won't contact you on the back of
a community post, they would not know who you are or you
contact details from your community login Saying your office has technical issues for now.
I am moving soon and would still like to have sky in 3 rooms as l do
now .
The SerpApi Model Context Protocol (MCP) server provides a unified search tool for AI agents.
It's also worth taking a look at our Bing Playground and performing a few searches to see it all in action. Returned
in the relatedSearches.value key (array of related searches)
in the official API, our API returns the equivalent in the top level related_searches key (array of related searches).
gibt Spielern die Möglichkeit, durch ranglistenbasierte Herausforderungen beträchtliche
Beträge zu gewinnen. Im Karamba Casino steht das Wohlbefinden der Spieler an oberster Stelle.
Mit zuverlässiger Hilfe jederzeit zur Hand können Sie sich ganz auf das Spielen Ihrer Lieblingsspiele konzentrieren. Karamba legt zudem Wert auf Vielfalt und bietet
mehrsprachige Unterstützung, um Spielern aus aller Welt gerecht zu werden. Die
Plattform bietet einen Rund-um-die-Uhr-Support, damit Sie stets die nötige Hilfe bekommen.
Egal, was Sie spielen, die Atmosphäre und das Bild des Projekts werden auf einem
sehr hohen Qualitätsniveau sein. Laden Sie Ihre Freunde ein, bei zahlreichen Gelegenheiten zusammenzuspielen oder teilen Sie
Ihre Emotionen mit anderen Benutzern aus der ganzen Welt. Beschäftigte
Spieler werden mit dem ?Autospielen“-Modus zufrieden sein. Aber es
bedeutet nicht, dass der Benutzer sie nur spielen muss, weil es auch fünf
Walzen gibt.
Sie bieten insgesamt 200 ? für die erste Einzahlung plus 100
Freispiele, wenn wir alle drei Einzahlungsboni zählen. Der beste,
sicherste und schnellste Weg, um herauszufinden, ob Sie in einem Land leben,
auf das Sie wetten dürfen Karamba online ist zu Überprüfen Sie unsere Casino-Angebote.
Registrieren Sie sich daher nicht und spielen Sie nicht,
wenn es in Ihrem Land gesetzliche Beschränkungen gibt.
bei denen Stammspieler exklusive Vorteile wie höhere Auszahlungslimits,
persönliche Betreuung und Bonusprämien erhalten. Dadurch steht Spielern eine breite Palette
an Spielautomaten, Tischspielen und Live-Casino-Angeboten zur
Verfügung. Dank regelmäßiger Aktionen und Promotionen bleibt das Casino auch für Stammspieler interessant.
Die Plattform bietet über 2.000 Spiele, darunter Slots, Tischspiele und Live-Dealer-Optionen. Die Plattform bietet eine beeindruckende Auswahl von über 3.500 Spielen, darunter zahlreiche Slots, Tischspiele und Live-Casino-Angebote.
GetSlots ist ein Online Casino, das zur Dama N.V.
Online Casino Gruppe gehört und von Curacao reguliert und lizenziert wird.
Das Layout ist minimalistisch und bietet eine großartige Leistung,
wenn es um eine einfache Navigation und verbesserte Ladezeiten geht.
Betrieben und ist das Schwestercasino von Betchan Casino
(von N1 Interactive). Durchsuche die Spiele-Lobby und du
wirst auf Slots-Spiele, Tischspiele, Jackpot-Spiele, Live-Casino-Spiele und Bitcoin-Spiele für ein abwechslungsreiches Gameplay stoßen.
by binding to the ghrelin receptor in the pituitary gland.
When used alone it can increase muscle mass, improve recovery and enhance overall well?being, but many users
combine it with CJC?1295, another growth?hormone?releasing peptide
(GHRP). The combination is popular among athletes,
bodybuilders and people seeking anti?aging benefits because the two molecules work together to produce a more pronounced release of growth hormone than either can achieve alone.
Below you will find an in?depth look at the side effects that can arise from using
CJC?1295 and ipamorelin together, as well as why
peptides are chosen over other substances for these purposes.
The Synergistic Effects of Ipamorelin and CJC 1295: What
You Need to Know
When ipamorelin and CJC?1295 are injected simultaneously or sequentially,
the two peptides create a feedback loop that amplifies
growth?hormone secretion. Ipamorelin acts as a potent ghrelin receptor agonist
while CJC?1295 stabilizes growth hormone?binding protein 2 (GHBP),
which prolongs the half?life of circulating growth hormone.
The result is an initial spike in GH levels followed by
sustained elevations that can last for several
hours. This synergy can lead to more rapid muscle
protein synthesis, greater fat loss and improved tissue repair compared with either peptide alone.
The Synergistic Effects of Ipamorelin and CJC 1295: What
You Need to Know
Because the combined effect is stronger than the sum of its parts, users often experience a higher incidence of side effects.
The most common adverse reactions are related to fluid retention, joint pain,
swelling in the extremities (especially hands and feet) and a feeling of fullness or bloating.
These symptoms arise from increased vascular permeability and extracellular fluid accumulation caused by high levels
of growth hormone and insulin?like growth factor?1 (IGF?1).
In some cases, users report headaches, dizziness or mild nausea shortly after
injection; these are usually transient but can be more pronounced when both peptides are taken together.
Why Peptides?
Peptides offer a number of advantages over traditional anabolic steroids or
other performance enhancers. First, they act directly on the endocrine system, mimicking naturally occurring hormones and therefore producing fewer long?term disruptions to the body’s own hormone production.
Second, because peptides such as ipamorelin and CJC?1295
are small molecules that bind specific receptors, they
tend to have a lower risk of off?target effects
compared with broad?acting drugs. Third, peptides can be delivered in very low doses (often measured in micrograms), which reduces the
likelihood of serious side effects while still achieving therapeutic benefits.
Finally, peptides do not typically carry the same legal or anti?doping penalties that steroids do,
making them attractive for athletes who want to stay within regulatory boundaries.
Common Side Effects of CJC 1295 and Ipamorelin
Fluid Retention ? Users frequently report swelling in the ankles, calves or wrists, as well as
a general sense of puffiness. This is largely due to increased production of IGF?1 and its effect on sodium retention.
Joint Pain and Stiffness ? The accumulation of fluid around joints can cause discomfort
or reduced range of motion, especially in the knees and shoulders.
Headaches ? Some individuals experience tension?type headaches within a few hours after injection;
these usually resolve within 24?48?hours.
Nausea and Dizziness ? These symptoms are less common but can occur when growth hormone levels rise
rapidly, especially if the dose is too high or the injection technique
is improper.
Local Injection Site Reactions ? Redness, swelling or
mild pain at the injection site may appear for a day or two; this can be mitigated by
rotating sites and using proper aseptic technique.
Sleep Disturbances ? A minority of users report difficulty falling asleep or vivid dreams during the
night, possibly linked to increased metabolic activity
induced by growth hormone.
Managing Side Effects
Dose Titration: Starting with a low dose (e.g., 0.1?mg ipamorelin and 0.5?mg CJC?1295) and gradually increasing helps the body adapt while minimizing side effects.
Hydration & Electrolytes: Maintaining adequate water intake and electrolytes can counteract
fluid retention and reduce joint swelling.
Compression Gear: Wearing compression sleeves or stockings may help alleviate edema in the limbs.
Timing of Injections: Administering injections at night or early morning can reduce daytime discomfort and
improve sleep quality.
Monitoring Hormone Levels: Regular blood tests
for GH, IGF?1, insulin and thyroid function allow adjustments before
side effects become problematic.
Long?Term Considerations
While short?term use of ipamorelin and CJC?1295 is generally well tolerated, chronic
administration may lead to desensitization of ghrelin receptors or
altered growth hormone receptor sensitivity. Additionally, prolonged elevation of
IGF?1 has been linked in some studies to increased
cancer risk, although the data are not conclusive for peptide therapy alone.
Users should therefore employ periodic breaks (cycles) and maintain regular medical check?ups.
In summary, the combination of ipamorelin and CJC?1295 delivers a potent growth?hormone boost that can accelerate
muscle gain, fat loss and tissue repair. The synergy also amplifies certain side effects such as fluid retention, joint pain and headaches.
Proper dosing, injection technique, hydration strategies and medical monitoring can help mitigate these risks.
Peptides remain attractive for their targeted action,
lower systemic toxicity compared to steroids, and the ability to produce benefits at low dosages while staying within many regulatory frameworks.
Anavar 20mg Only Cycle
When athletes and bodybuilders seek a subtle lift in muscle definition without the hefty side effects
of higher dosage anabolic steroids, an "Anavar 20?mg only cycle" becomes a popular
choice. This regimen is built around the compound oxandrolone, commonly marketed as Anavar, which
is prized for its mild potency and impressive ability to enhance strength while preserving lean body mass.
Why 20?mg?
The typical therapeutic dose of oxandrolone ranges from 5?10?mg per day, but when used in bodybuilding contexts, users often start with a conservative 20?mg daily.
This dosage offers several benefits:
Low androgenic activity: It minimizes the risk of virilization and other side effects associated with stronger anabolic steroids.
High lipophilic profile: Oxandrolone is well absorbed orally, ensuring
consistent blood levels without the need for injections.
Cumulative effect over time: Even at modest doses,
the cumulative anabolic effect can become significant when paired with an optimal diet and training regimen.
2.2 Choosing a Diet: Low?Carb vs. Moderate?Protein
Low?Carbohydrate (Low?Carb) Approach
A low-carb diet focuses on reducing carbohydrate intake while maintaining or increasing
protein consumption. Its key features include:
Ketosis Induction: By limiting carbs, the body shifts to burning fat as a primary fuel source.
Insulin Suppression: Lower carb intake results in reduced insulin spikes, promoting fat loss and preserving muscle glycogen more
efficiently for workouts.
Reduced Caloric Intake: Often, lower-carb diets lead to a natural reduction in calories due to decreased appetite or food volume.
Potential Benefits for the Bodybuilder:
Enhanced Fat Oxidation During Workouts: The body can more readily access stored fat during exercise, potentially improving endurance.
Reduced Substrate Competition: With less carbohydrate available, glycogen stores are preserved for high-intensity work.
Increased Leptin and Ghrelin Regulation: Improved satiety hormones
could aid in maintaining a lean physique.
Possible Drawbacks:
Limited Glycogen Reserves: Reduced carb intake may limit the
total amount of glycogen available, which can compromise very high-intensity or prolonged training sessions.
Nutrient Density Concerns: Some carbohydrate-rich
foods also provide essential micronutrients; a low-carb approach might reduce overall nutrient
density unless carefully planned.
3.4 The Role of Protein
Protein’s primary role is muscle repair and growth, but it also provides an energy source when carbohydrates are insufficient.
For athletes engaged in intense training, protein requirements are
higher than for sedentary individuals?generally ranging from 1.2?2.0 g/kg body weight/day, depending
on training load.
In a low-carb context, adequate protein intake is critical
to maintain lean mass and support metabolic processes.
Protein also influences satiety, which can be beneficial when caloric intake must be controlled.
---
4. Practical Recommendations for the Athlete
4.1 Macronutrient Targets
Metric Low-Carb Goal (20?30?g net carbs)
Carbohydrate 150?200?kcal (? 37?50?g) per day
Protein 2.0?2.5?g/kg body weight (~ 140?175?kg for a 70?kg athlete)
Fat Remaining calories, typically ~1.3?1.6?g/kg body weight
(~90?112?kg)
Protein: Prioritize high-quality sources (lean meats, fish,
dairy, eggs). Consider protein shakes or bars if needed to meet targets.
Fat: Include unsaturated fats (olive oil, nuts, seeds, fatty fish) for essential fatty
acids and satiety. Use saturated fats sparingly.
4.3 Timing of Nutrient Intake
Timing Recommendation
Pre?Workout (30?60?min before) Small protein snack (~15?20?g) to provide amino acids during exercise; optional low?carb carbohydrate if
energy level is low.
During Workout If session >90?min, consider a protein drink (~10?15?g).
Avoid high?fat or fiber foods that may cause GI discomfort.
Post?Workout (within 30?min) Consume ~25?30?g of protein (preferably whey or
hydrolyzed protein) to stimulate muscle repair and growth.
Evening Light protein source (~20?25?g) such as cottage cheese,
Greek yogurt, or a small portion of lean meat before
bed.
Key Take?aways
Protein is the cornerstone of a low?carb training plan; aim
for 1.5?2?g per kg of body weight.
Carb intake should be restricted to around 20?50?g per day (or <30?% of calories) if you are on a ketogenic diet, but may be higher (~80?100?g) if your goal is to maintain high training intensity while still being low in carbs.
Fat should fill the remaining calorie gap and support hormone production, especially during prolonged fasting or sleep.
3. How To Use Calorie Counting When You’re Low?Carb
A. Establish Your Baseline
Determine your BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate) using an online calculator (Mifflin?St Jeor equation is reliable).
Add activity factor:
- Sedentary: ×1.2
- Lightly active: ×1.375
- Moderately active: ×1.55
- Very active: ×1.725
- Extra active (heavy training): ×1.9
This gives your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE).
B. Set Your Macro Ratios
For most people: Carbs 20?30%, Protein 25?35%, Fat 40?55%.
Use a calculator or spreadsheet to convert percentages into grams:
- Carbs & protein = 4 kcal/g
- Fat = 9 kcal/g
C. Track Calories & Macros
Apps: MyFitnessPal, Cronometer, Lose It!
Food diary: Record all meals and snacks; weigh or estimate portions.
Adjust weekly: If you’re not seeing the desired changes (weight loss, muscle gain), tweak calorie intake by ±200 kcal.
4. Common Questions & Practical Tips
Question Short Answer
Do I need a supplement? Not necessary if your diet is balanced. Vitamin?D, B12, and protein powders can help fill gaps but are optional.
Can I eat out and still meet my goals? Yes?look for dishes with lean proteins (chicken breast, fish), vegetables, and whole grains. Watch sauces and dressings that add hidden calories.
How do I keep it interesting? Rotate protein sources (pork, beef, lamb, tofu) and use different spices or marinades to vary flavor.
Is a low?carb diet okay for me? The carnivore approach is very low in carbs. If you notice fatigue or digestive changes, consider adding small portions of vegetables or legumes.
Do I need supplements? A balanced diet usually covers most nutrients. Vitamin D and B12 can be monitored if your intake is uncertain.
---
5?? Quick?Reference Checklist (Before Every Meal)
Check Portion Sizes
- 100?g of meat → ~250?kcal
- 50?g of fat → ~450?kcal
Confirm Protein & Fat Balance
- Aim for 25?30?% protein, 70?75?% fat if using a 2000?kcal daily target.
Track Calories (use an app or food diary).
Add Dairy if Needed ? 1 cup of full?fat yogurt ? 150?kcal + 7?g protein.
Hydrate ? Water is best; limit sugary drinks.
Adjust Portion Size based on satiety and daily energy needs.
Bottom?Line
Protein: 1?2?g per kg body weight (?50?70?g for a 70?kg person).
Calories: Roughly 30?35?kcal per kg of body weight (~2100?2450?kcal/day) if you want to gain ~0.5?kg/yr, or 25?30?kcal/kg (~1750?2100?kcal/day) for a leaner build.
Macros: 20?25% protein (?100?120?g), 20?35% fat (?45?65?g), remaining carbs.
Use these guidelines as a starting point, then adjust based on your actual progress and how you feel.
Good luck on your journey!