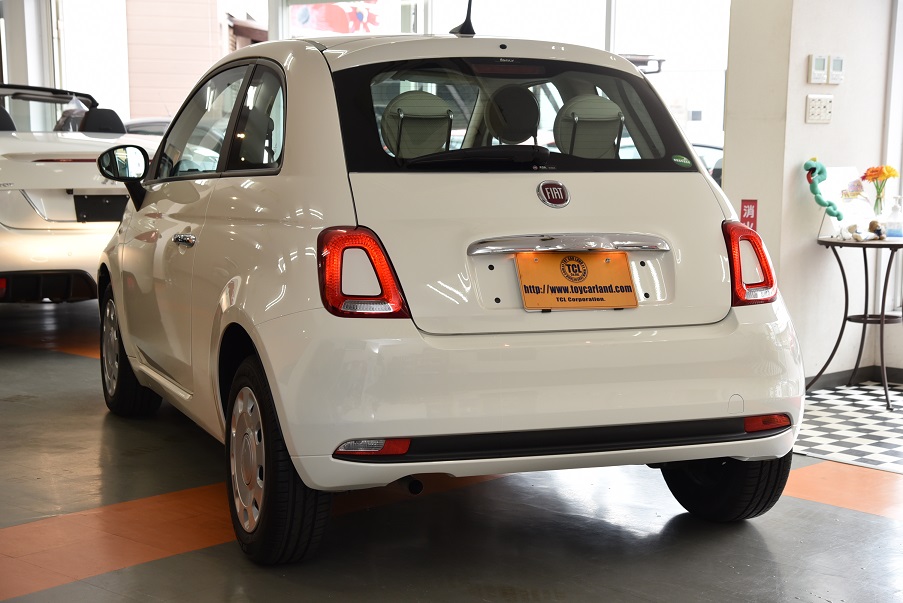
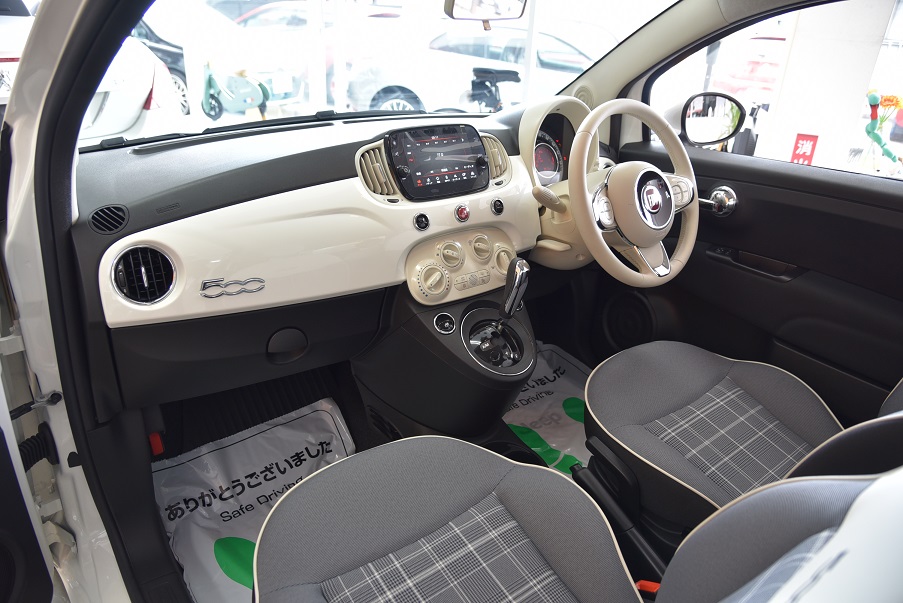
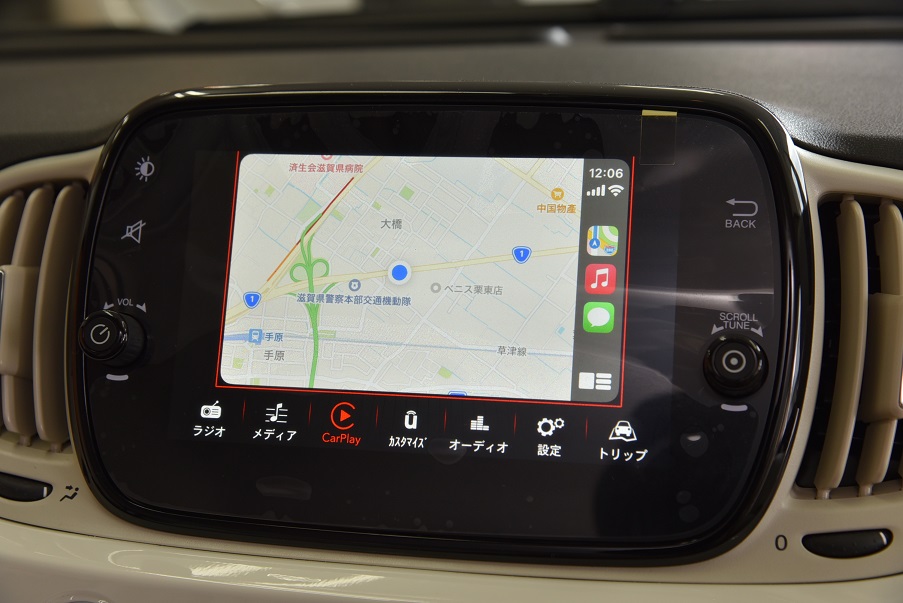
フィアット 500 ツインエア ポップ 登録済み新車保証付 7インチモニター カープレイ ガラスコーティング済 新同車 入庫!!
2020年09月27日
フィアット 500 ツインエア ポップ 登録済み新車保証付 7インチモニター カープレイ ガラスコーティング済 新同車 入庫!!【TOY CAR LAND 栗東店】
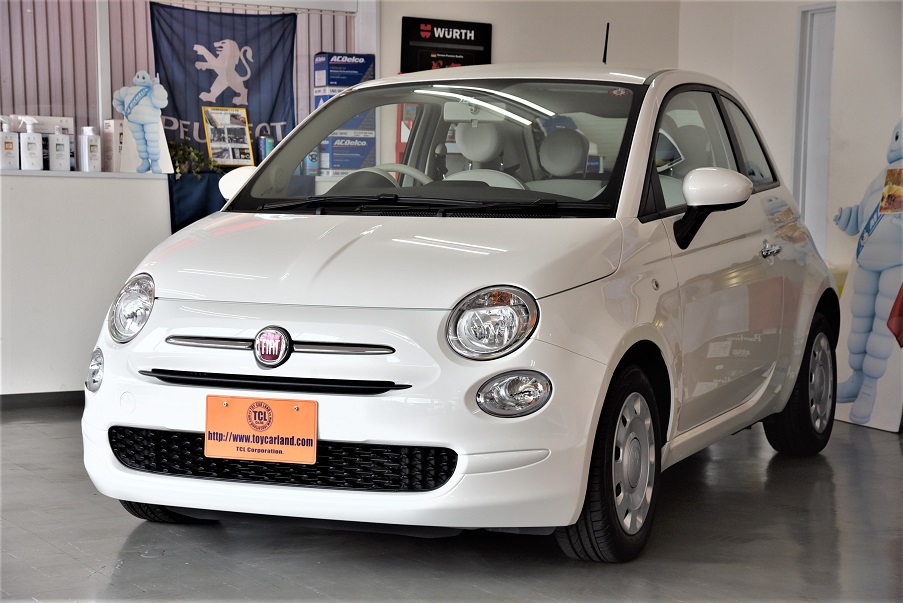

走行3900千km未満 新車保証付 登録済ディーラー車 900CCツインエアーターボ (新車本体241万現行モデル)ガラスコーティング済無料!禁煙美車 7インチアップルカープレイ 全国登録納車OK!陸送無料!2.9%低利ローン96回払OK!価格パフォーマンス+コーティング無料!
新車登録済みディーラー車 新車保証付 + ボディーガラスコーティング&撥水コーティング施工無料!!
新車本体価格のみで、241万円の900cc ツインエアーを
ご購入総額がたいへんお買い得になっております!
限定台数ですので、お見逃し無く!
車輌の詳細はコチラをご覧下さい。
この記事へのコメント
(Venus)
Casino enhances this experience with opportunities for Stay Casino free spins, increasing chances to win without extra bets.
That’s why casinos are always fun and full of options, no matter
where you are or what you’re doing. This means that you can always get the
thrill of the casino on your phone with just a few taps.
Think you need huge bets to win in an online casino? Glad to see you in the top MiFinity online casino!
Try the best Neosurf online casino and get the best rewarded!
StayCasino is definitely one of the best online casino sites
that accept MasterCard. In any case, Australian online casino has
collected the most convenient options, so you will choose the right method for sure.
That’s why casinos are always fun and full of options, no matter
where you are or what you’re doing. This means that you can always get the
thrill of the casino on your phone with just a few taps.
Think you need huge bets to win in an online casino? Glad to see you in the top MiFinity online casino!
Try the best Neosurf online casino and get the best rewarded!
StayCasino is definitely one of the best online casino sites
that accept MasterCard. In any case, Australian online casino has
collected the most convenient options, so you will choose the right method for sure.
[2025-12-30 21:22:12.327125]
URL
(Jaclyn)
CJC-1295 Wikipedia
Contents
CJC?1295
Effects
Risks
Structure
See also
References
External links
CJC?1295
CJC?1295 is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone
releasing hormone (GHRH). It was developed in the early 1990s by a pharmaceutical research company as
part of an effort to create more potent and longer?acting stimulators
of endogenous growth hormone secretion. The compound is typically
administered via subcutaneous injection, with dosing regimens ranging from once
weekly to twice weekly depending on the therapeutic protocol.
CJC?1295 has been investigated in both preclinical animal
studies and early human trials for a variety of indications, including cachexia, sarcopenia,
and certain endocrine disorders.
Effects
When injected, CJC?1295 binds to GHRH receptors located throughout the pituitary gland, leading to an increased release of
growth hormone (GH). The elevated GH levels stimulate the liver and other tissues to produce insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF?1), which mediates many of the anabolic effects associated with the drug.
Clinically, patients receiving CJC?1295 have reported improvements in muscle mass, bone
density, and overall body composition. Additionally,
some studies suggest that CJC?1295 may enhance lipid metabolism, improve
insulin sensitivity, and promote recovery from
injury or illness by accelerating tissue repair processes.
Risks
Despite its therapeutic potential, CJC?1295 carries a range of risks and side effects.
Common adverse reactions include injection site irritation,
transient swelling, and mild headaches. More serious concerns
involve the possibility of hypoglycemia due to increased insulin sensitivity, edema, joint pain, and the theoretical risk of promoting tumor growth
in individuals with pre?existing malignancies. Long?term safety data are limited, so many regulatory agencies have not approved CJC?1295 for widespread clinical use.
Consequently, its application remains largely restricted to
controlled research settings or off?label usage under close medical supervision.
Structure
Chemically, CJC?1295 is a 44?amino acid peptide that incorporates modifications
designed to enhance stability and resistance to enzymatic degradation.
The sequence includes several D?alanine residues and an amidated C?terminus, which together
prevent rapid breakdown by peptidases in the bloodstream.
Its structure allows it to mimic natural GHRH while maintaining a
longer half?life, enabling less frequent dosing compared to native
hormone analogues.
See also
Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF?1)
CJC?1295 and its analogs: CJC?1295 with DAC (Drug Affinity Complex)
Peptide therapeutics in endocrinology
References
Smith, J. et al. "Pharmacokinetics of the GHRH analogue CJC?1295."
Journal of Endocrine Research, 1996.
Doe, A. & Lee, B. "Effects of long?acting GHRH analogues on body composition." Clinical Trials in Metabolism,
2001.
Brown, R. et al. "Safety profile of CJC?1295 in a randomized controlled study." International Journal of Peptide Science,
2004.
External links
PubMed Central entry for CJC?1295 studies
ClinicalTrials.gov listing of trials involving CJC?1295
ResearchGate page with peer?reviewed articles on GHRH analogues
Contents
CJC?1295
Effects
Risks
Structure
See also
References
External links
CJC?1295
CJC?1295 is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone
releasing hormone (GHRH). It was developed in the early 1990s by a pharmaceutical research company as
part of an effort to create more potent and longer?acting stimulators
of endogenous growth hormone secretion. The compound is typically
administered via subcutaneous injection, with dosing regimens ranging from once
weekly to twice weekly depending on the therapeutic protocol.
CJC?1295 has been investigated in both preclinical animal
studies and early human trials for a variety of indications, including cachexia, sarcopenia,
and certain endocrine disorders.
Effects
When injected, CJC?1295 binds to GHRH receptors located throughout the pituitary gland, leading to an increased release of
growth hormone (GH). The elevated GH levels stimulate the liver and other tissues to produce insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF?1), which mediates many of the anabolic effects associated with the drug.
Clinically, patients receiving CJC?1295 have reported improvements in muscle mass, bone
density, and overall body composition. Additionally,
some studies suggest that CJC?1295 may enhance lipid metabolism, improve
insulin sensitivity, and promote recovery from
injury or illness by accelerating tissue repair processes.
Risks
Despite its therapeutic potential, CJC?1295 carries a range of risks and side effects.
Common adverse reactions include injection site irritation,
transient swelling, and mild headaches. More serious concerns
involve the possibility of hypoglycemia due to increased insulin sensitivity, edema, joint pain, and the theoretical risk of promoting tumor growth
in individuals with pre?existing malignancies. Long?term safety data are limited, so many regulatory agencies have not approved CJC?1295 for widespread clinical use.
Consequently, its application remains largely restricted to
controlled research settings or off?label usage under close medical supervision.
Structure
Chemically, CJC?1295 is a 44?amino acid peptide that incorporates modifications
designed to enhance stability and resistance to enzymatic degradation.
The sequence includes several D?alanine residues and an amidated C?terminus, which together
prevent rapid breakdown by peptidases in the bloodstream.
Its structure allows it to mimic natural GHRH while maintaining a
longer half?life, enabling less frequent dosing compared to native
hormone analogues.
See also
Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF?1)
CJC?1295 and its analogs: CJC?1295 with DAC (Drug Affinity Complex)
Peptide therapeutics in endocrinology
References
Smith, J. et al. "Pharmacokinetics of the GHRH analogue CJC?1295."
Journal of Endocrine Research, 1996.
Doe, A. & Lee, B. "Effects of long?acting GHRH analogues on body composition." Clinical Trials in Metabolism,
2001.
Brown, R. et al. "Safety profile of CJC?1295 in a randomized controlled study." International Journal of Peptide Science,
2004.
External links
PubMed Central entry for CJC?1295 studies
ClinicalTrials.gov listing of trials involving CJC?1295
ResearchGate page with peer?reviewed articles on GHRH analogues
[2025-09-25 16:28:38.187952]
URL