人気クリーンディーゼルターボ!フレンチワゴン!プジョー308SWアリュール ブルーHDi 走行18千km美車 入庫!
2021年05月29日
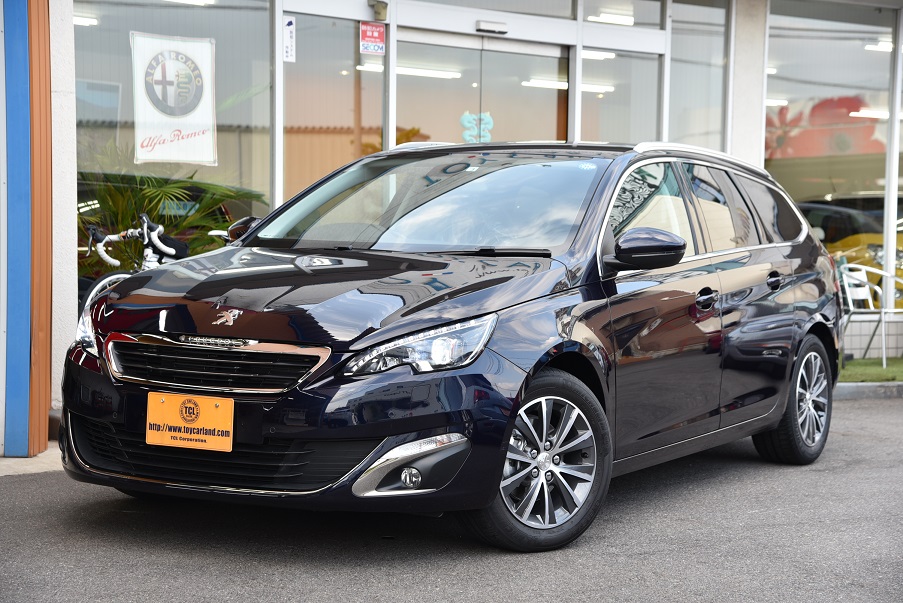
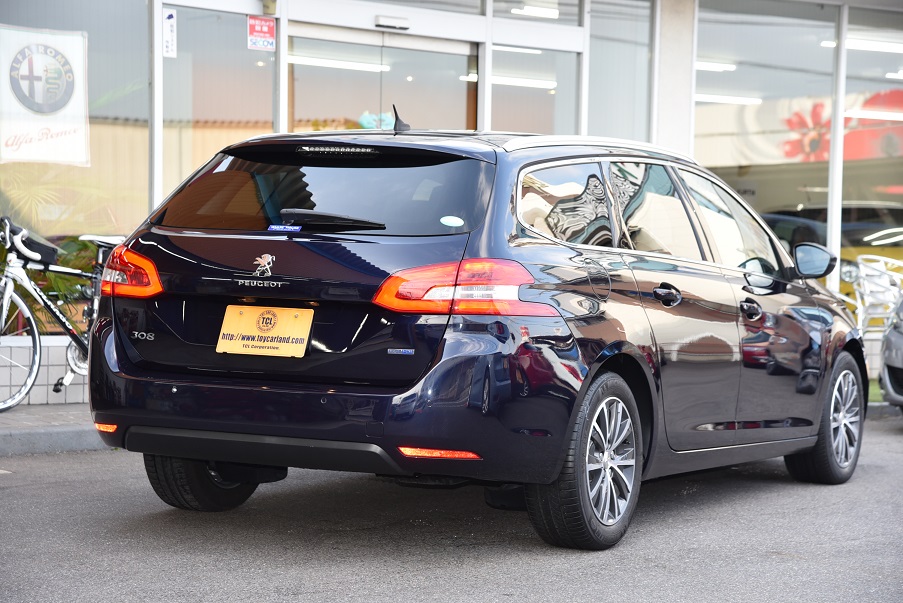
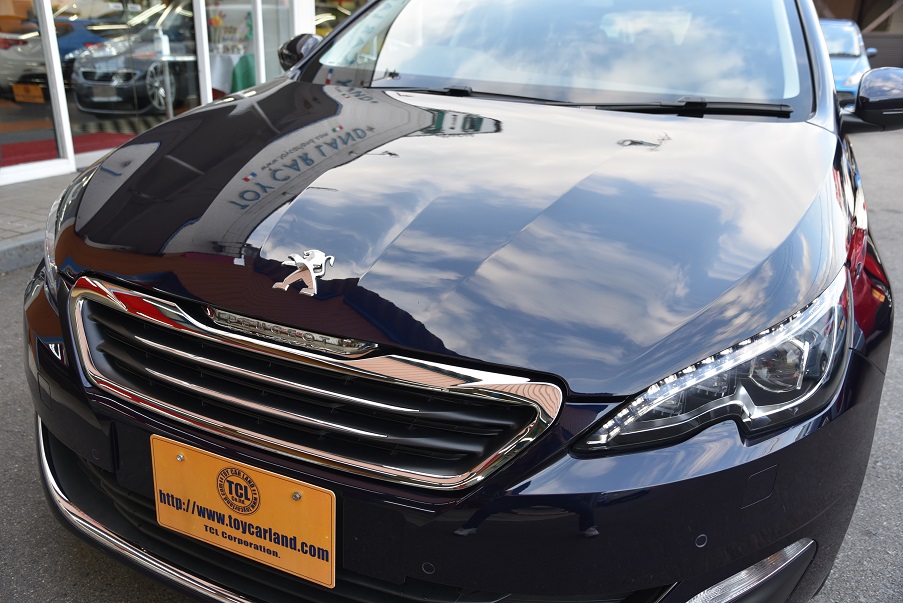
人気クリーンディーゼルターボ!
フレンチワゴン!プジョー308SWアリュール ブルーHDi 走行18千km美車 入庫!
1600cc クリーンディーゼルターボ 6AT ガラスコーティング済 禁煙美車 走行少18千km 衝突軽減ブレーキ アクティブクルコン LEDライト タッチパネルコントロールモニター ETC Bluetooth Bモニター Pソナー パドルシフト 人気フレンチワゴン入庫!
ボディーコーティング済み 禁煙美車 ピッカピカです
ホント、良いクルマです・・・
車輌の詳細、特選車価格、詳細画像はコチラをご覧下さい。
この記事へのコメント
(Abdul)
Crown is the ultimate destination for first-class dining experiences.
Discover Crown Towers Melbourne with a truly iconic experience.
One (1) wedding gift will be delivered to your room during your stay.
2pm check-out is automatically applied during the booking process.
Passenger carrying charter flights are conducted under day VFR rules and are limited to daylight operations only.
Momondo compares 3M+ hotel and accommodation options.
We believe that?together we create unforgettable experiences
for our guests. We are also committed to proving a culture
that motivates, challenges, and inspires our colleagues every day.
Discover Crown Towers Melbourne with a truly iconic experience.
One (1) wedding gift will be delivered to your room during your stay.
2pm check-out is automatically applied during the booking process.
Passenger carrying charter flights are conducted under day VFR rules and are limited to daylight operations only.
Momondo compares 3M+ hotel and accommodation options.
We believe that?together we create unforgettable experiences
for our guests. We are also committed to proving a culture
that motivates, challenges, and inspires our colleagues every day.
[2025-12-27 23:03:02.641278]
URL
(Minda)
Ideal for couples, business travellers, or staycations, Crown Metropol offers sleek design, modern amenities, and direct access to restaurants
and gaming. Earn and redeem points across gaming, hotels, restaurants, and more ? online and on-site.
Conveniently located in the centre of Perth,
Novotel Perth Murray Street offers free WiFi throughout the property and a bar.
Crown Perth offers a spectacular array of world-class restaurants
and fine dining experiences.
Three world-class hotels, one unforgettable stay ? luxury,
comfort, and style in the heart of Western Australia’s premier entertainment resort.
Just show your Crown Rewards Card when you pay or
play and you can start earning points, which you can redeem for Crown experiences like dining, gaming, hotel stays and much more.
Points can be used to pay for almost everything at Crown Perth and Crown Melbourne, like shopping, dining, gaming, hotel stays and much more.
You can use your Card at participating restaurants, bars,
hotels and more, every time you visit Crown. Plus, indulge on your birthday with your Crown Rewards Member
discounted rates and complimentary birthday inclusions at one of
Crown Perth’s luxury hotels. Real reviews from guests who experienced the luxury, entertainment, and world-class
service at Crown Perth in Western Australia.
and gaming. Earn and redeem points across gaming, hotels, restaurants, and more ? online and on-site.
Conveniently located in the centre of Perth,
Novotel Perth Murray Street offers free WiFi throughout the property and a bar.
Crown Perth offers a spectacular array of world-class restaurants
and fine dining experiences.
Three world-class hotels, one unforgettable stay ? luxury,
comfort, and style in the heart of Western Australia’s premier entertainment resort.
Just show your Crown Rewards Card when you pay or
play and you can start earning points, which you can redeem for Crown experiences like dining, gaming, hotel stays and much more.
Points can be used to pay for almost everything at Crown Perth and Crown Melbourne, like shopping, dining, gaming, hotel stays and much more.
You can use your Card at participating restaurants, bars,
hotels and more, every time you visit Crown. Plus, indulge on your birthday with your Crown Rewards Member
discounted rates and complimentary birthday inclusions at one of
Crown Perth’s luxury hotels. Real reviews from guests who experienced the luxury, entertainment, and world-class
service at Crown Perth in Western Australia.
[2025-12-27 08:43:59.432485]
URL
(Renaldo)
Im Live-Casino warten klassische Tischspiele wie Roulette, Blackjack, Baccarat und Poker in zahlreichen internationalen Varianten auf Sie.
Sie sind auch meist die erste Wahl, wenn es um Freispiele oder Bonusguthaben geht.
Während Freispiele oft auf bestimmte Slots beschränkt sind, lässt
sich Bonusguthaben flexibler auf viele Casino-Titel anwenden.
Dass bestimmte Spiele nicht mit Bonusgeldern genutzt werden können, ist ebenfalls eine Einschränkung,
die in fast allen Online Casinos gilt. Durch Freispiele oder ein kostenloses Spielguthaben wird
diese Hürde überwunden, und die User können sich ganz ohne eine eigene
Investition mit dem Casino und seinen Angeboten vertraut machen.
Gelingt es Usern, mit solchen Bonus-Angeboten Geld zu gewinnen und die Umsatzbedingungen zu erfüllen, so können sich diese User den Gewinn auszahlen lassen, ohne jemals eine Einzahlung getätigt zu haben. Stellt ein Online Casino ganz ohne
eigene Einzahlung direkt nach der Registrierung Bonus Guthaben oder Freispiele zur Verfügung, so geht
das Casino damit ein Risiko ein. Da Sie vorher noch keine Einzahlung getätigt haben,
stehen Ihnen nicht alle in dem Casino angebotenen Zahlungsmethoden für
die Auszahlung zur Verfügung. Nachdem Sie diesen Umsatz generiert haben, wird
das Bonusgeld automatisch auf das Echtgeldkonto verschoben.
Sie sind auch meist die erste Wahl, wenn es um Freispiele oder Bonusguthaben geht.
Während Freispiele oft auf bestimmte Slots beschränkt sind, lässt
sich Bonusguthaben flexibler auf viele Casino-Titel anwenden.
Dass bestimmte Spiele nicht mit Bonusgeldern genutzt werden können, ist ebenfalls eine Einschränkung,
die in fast allen Online Casinos gilt. Durch Freispiele oder ein kostenloses Spielguthaben wird
diese Hürde überwunden, und die User können sich ganz ohne eine eigene
Investition mit dem Casino und seinen Angeboten vertraut machen.
Gelingt es Usern, mit solchen Bonus-Angeboten Geld zu gewinnen und die Umsatzbedingungen zu erfüllen, so können sich diese User den Gewinn auszahlen lassen, ohne jemals eine Einzahlung getätigt zu haben. Stellt ein Online Casino ganz ohne
eigene Einzahlung direkt nach der Registrierung Bonus Guthaben oder Freispiele zur Verfügung, so geht
das Casino damit ein Risiko ein. Da Sie vorher noch keine Einzahlung getätigt haben,
stehen Ihnen nicht alle in dem Casino angebotenen Zahlungsmethoden für
die Auszahlung zur Verfügung. Nachdem Sie diesen Umsatz generiert haben, wird
das Bonusgeld automatisch auf das Echtgeldkonto verschoben.
[2025-12-20 15:01:21.226102]
URL
(Paulette)
Anavar Cycle: Vital Information For Optimal Results & Usage
A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Your Strength?Training Cycle
Strength training is an art that blends physiology,
nutrition, recovery, and mindset. Whether you’re a seasoned powerlifter or just starting
out on the gym floor, mastering each element of your cycle can turn raw effort into measurable gains.
This guide walks through every stage?from planning and periodization to nutrition, supplementation, rest, and
mental preparation?so you can design a training program that’s not
only effective but also sustainable.
> Disclaimer
> The information below is for educational purposes only.
It does not replace professional medical or sports?specific advice.
Consult with a certified coach, physician, or registered dietitian before making
significant changes to your training or dietary routine,
especially if you have any health conditions.
---
1. Planning & Periodization
1.1 Establish Clear Goals
Short?term: e.g., "Increase bench press by 5?kg in the next 6 weeks."
Long?term: e.g., "Win a local bodybuilding competition in 12 months."
Write your goals SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant,
Time?bound). Keep them visible.
1.2 Macro?cycle Design
Divide your training into three overlapping cycles:
Cycle Duration Focus
Macro?cycle 12?24?weeks (overall plan) Overall strength/size progression
Meso?cycle 4?6?weeks Phase-specific goals:
hypertrophy, peaking, recovery
Micro?cycle 1 week Weekly training plan (sessions, loads, volumes)
1.3 Load Progression Template
Use a simple "5/3/1" style progression:
Week 1 ? Light load (60?% 1RM), high reps (12?15)
Week 2 ? Moderate load (70?% 1RM), moderate reps (8?10)
Week 3 ? Heavy load (80?% 1RM), low reps (4?6)
Week 4 ? Deload ? 50?% 1RM, 12?15 reps
Add a "percentage + rep" matrix:
Load % Reps
60% 12?15
70% 8?10
80% 4?6
This is the "load?repetition schedule".
3.2 "Intensity" vs "Volume"
Intensity = % of 1RM (or equivalent).
Volume = Total work = Intensity × Reps × Sets.
Example: 3 sets of 12 reps at 60% → Volume = 3×12×0.6 =
21.6 units.
In a weekly plan, you might target an overall volume goal and then break it into daily
intensity blocks (e.g., low intensity on day 1, moderate on day 2,
high on day 3).
3.3 "Progressive Overload" Quantified
A common overload method:
Linear progression: Add ~2?5% of 1RM each week or increase reps by 2 until
a ceiling is reached.
For example, if your current 5RM is 70?kg:
Week?1: 70?kg × 5
Week?2: 72.5?kg × 5 (?+3.5%)
Week?3: 75?kg × 5
You can also use percentage tables: e.g., week?1
= 80%, week?2 = 82%, etc.
4. Sample Weekly Routine for a Novice Lifter
Day Exercise Sets Reps Load
Mon Back Squat (or Front Squat) 3 5 70?75?% of 1RM
Tue Bench Press 3 5 70?75?% of 1RM
Thu Deadlift (conventional or sumo) 2 5 75?80?% of 1RM
Fri Overhead Press + Pull?Ups/Rows 3 5 70?75?% of 1RM
(for press)
Warm?up: 10?15 min light cardio, dynamic stretches.
Progression: Add ~2.5?kg to upper body lifts or 5?kg to lower body each week if you
can complete all reps with good form.
3. Nutrition
Calorie needs
Maintenance ? 13?15?kcal per kg body weight × 80?kg = 1040?1200?kcal (estimate).
Goal: Add ~250?300?kcal for lean mass gain → ~1300?1500?kcal/day.
Macronutrient split
Nutrient Goal Calories % of Total
Protein 2.2?g/kg → 176?g 704?kcal 50?55%
Carbs 4?5?g/kg → 320?400?g 1280?1600?kcal 45?55%
Fats 1.2?g/kg → 21?g 189?kcal 10?15%
Protein: 176?g ? 704?kcal
Carbohydrates: 400?g ? 1600?kcal
Fats: 20?g ? 180?kcal
Total ~3004?kcal (??3?000?kcal).
Why this works for a "tiny" body:
Low basal metabolic rate ? the body burns fewer calories at rest,
so even with minimal movement it needs a modest caloric
intake.
High energy density of foods ? 3000?kcal can be obtained from relatively small
volumes (e.g., 200?g protein shakes + 400?g fruit/vegetables
= ~1?2?L total).
Lean mass maintenance ? adequate protein preserves
muscle, which is critical for mobility and metabolic health.
Practical Implementation Tips
Goal Daily Plan Notes
General health 3000?kcal (?150?g protein) Focus on whole foods; incorporate dairy or fortified plant milk.
Body?building 3500?kcal (?200?g
protein) Add a post?workout shake (~30?g protein, 50?g carbs).
High activity 4000?kcal (?250?g protein) Split into 3?4 meals + snacks; consider
energy gels for long runs.
Keep a food log to track macros.
Adjust portion sizes if weight gain or loss is observed.
Hydrate adequately?especially important with higher caloric intake.
Key Take?aways
Situation Suggested Calories Protein
Sedentary 25?yr old, 190?lb, 5'10" ~2?100?2?200 kcal ~120?g (1.3?g/kg)
Light activity (walking/short workouts) +200?400 kcal Same protein target
Moderate training (strength or cardio) +400?600 kcal Maintain 120?g, increase to 140?160?g if muscle gain is goal
High?intensity or bulk phase +600?800 kcal 140?170?g
---
Practical Tips
Use a Food Diary / App ? Record meals for at least a week; this gives an accurate baseline.
Adjust Gradually ? Increase calories by ~100?200 per day if you’re not seeing desired changes after 1?2 weeks.
Track Body Weight & Composition ? If weight is stable and muscle gains are seen, calorie needs may be adequate.
Stay Hydrated & Sleep Well ? Both affect appetite regulation and energy expenditure.
Bottom Line
Your body requires roughly ??2100 kcal/day at rest (BMR) and about ??2600?2700 kcal/day when you factor in your typical activity level.
Start with that estimate, monitor progress, then adjust by small increments until you reach the desired results.
A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Your Strength?Training Cycle
Strength training is an art that blends physiology,
nutrition, recovery, and mindset. Whether you’re a seasoned powerlifter or just starting
out on the gym floor, mastering each element of your cycle can turn raw effort into measurable gains.
This guide walks through every stage?from planning and periodization to nutrition, supplementation, rest, and
mental preparation?so you can design a training program that’s not
only effective but also sustainable.
> Disclaimer
> The information below is for educational purposes only.
It does not replace professional medical or sports?specific advice.
Consult with a certified coach, physician, or registered dietitian before making
significant changes to your training or dietary routine,
especially if you have any health conditions.
---
1. Planning & Periodization
1.1 Establish Clear Goals
Short?term: e.g., "Increase bench press by 5?kg in the next 6 weeks."
Long?term: e.g., "Win a local bodybuilding competition in 12 months."
Write your goals SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant,
Time?bound). Keep them visible.
1.2 Macro?cycle Design
Divide your training into three overlapping cycles:
Cycle Duration Focus
Macro?cycle 12?24?weeks (overall plan) Overall strength/size progression
Meso?cycle 4?6?weeks Phase-specific goals:
hypertrophy, peaking, recovery
Micro?cycle 1 week Weekly training plan (sessions, loads, volumes)
1.3 Load Progression Template
Use a simple "5/3/1" style progression:
Week 1 ? Light load (60?% 1RM), high reps (12?15)
Week 2 ? Moderate load (70?% 1RM), moderate reps (8?10)
Week 3 ? Heavy load (80?% 1RM), low reps (4?6)
Week 4 ? Deload ? 50?% 1RM, 12?15 reps
Add a "percentage + rep" matrix:
Load % Reps
60% 12?15
70% 8?10
80% 4?6
This is the "load?repetition schedule".
3.2 "Intensity" vs "Volume"
Intensity = % of 1RM (or equivalent).
Volume = Total work = Intensity × Reps × Sets.
Example: 3 sets of 12 reps at 60% → Volume = 3×12×0.6 =
21.6 units.
In a weekly plan, you might target an overall volume goal and then break it into daily
intensity blocks (e.g., low intensity on day 1, moderate on day 2,
high on day 3).
3.3 "Progressive Overload" Quantified
A common overload method:
Linear progression: Add ~2?5% of 1RM each week or increase reps by 2 until
a ceiling is reached.
For example, if your current 5RM is 70?kg:
Week?1: 70?kg × 5
Week?2: 72.5?kg × 5 (?+3.5%)
Week?3: 75?kg × 5
You can also use percentage tables: e.g., week?1
= 80%, week?2 = 82%, etc.
4. Sample Weekly Routine for a Novice Lifter
Day Exercise Sets Reps Load
Mon Back Squat (or Front Squat) 3 5 70?75?% of 1RM
Tue Bench Press 3 5 70?75?% of 1RM
Thu Deadlift (conventional or sumo) 2 5 75?80?% of 1RM
Fri Overhead Press + Pull?Ups/Rows 3 5 70?75?% of 1RM
(for press)
Warm?up: 10?15 min light cardio, dynamic stretches.
Progression: Add ~2.5?kg to upper body lifts or 5?kg to lower body each week if you
can complete all reps with good form.
3. Nutrition
Calorie needs
Maintenance ? 13?15?kcal per kg body weight × 80?kg = 1040?1200?kcal (estimate).
Goal: Add ~250?300?kcal for lean mass gain → ~1300?1500?kcal/day.
Macronutrient split
Nutrient Goal Calories % of Total
Protein 2.2?g/kg → 176?g 704?kcal 50?55%
Carbs 4?5?g/kg → 320?400?g 1280?1600?kcal 45?55%
Fats 1.2?g/kg → 21?g 189?kcal 10?15%
Protein: 176?g ? 704?kcal
Carbohydrates: 400?g ? 1600?kcal
Fats: 20?g ? 180?kcal
Total ~3004?kcal (??3?000?kcal).
Why this works for a "tiny" body:
Low basal metabolic rate ? the body burns fewer calories at rest,
so even with minimal movement it needs a modest caloric
intake.
High energy density of foods ? 3000?kcal can be obtained from relatively small
volumes (e.g., 200?g protein shakes + 400?g fruit/vegetables
= ~1?2?L total).
Lean mass maintenance ? adequate protein preserves
muscle, which is critical for mobility and metabolic health.
Practical Implementation Tips
Goal Daily Plan Notes
General health 3000?kcal (?150?g protein) Focus on whole foods; incorporate dairy or fortified plant milk.
Body?building 3500?kcal (?200?g
protein) Add a post?workout shake (~30?g protein, 50?g carbs).
High activity 4000?kcal (?250?g protein) Split into 3?4 meals + snacks; consider
energy gels for long runs.
Keep a food log to track macros.
Adjust portion sizes if weight gain or loss is observed.
Hydrate adequately?especially important with higher caloric intake.
Key Take?aways
Situation Suggested Calories Protein
Sedentary 25?yr old, 190?lb, 5'10" ~2?100?2?200 kcal ~120?g (1.3?g/kg)
Light activity (walking/short workouts) +200?400 kcal Same protein target
Moderate training (strength or cardio) +400?600 kcal Maintain 120?g, increase to 140?160?g if muscle gain is goal
High?intensity or bulk phase +600?800 kcal 140?170?g
---
Practical Tips
Use a Food Diary / App ? Record meals for at least a week; this gives an accurate baseline.
Adjust Gradually ? Increase calories by ~100?200 per day if you’re not seeing desired changes after 1?2 weeks.
Track Body Weight & Composition ? If weight is stable and muscle gains are seen, calorie needs may be adequate.
Stay Hydrated & Sleep Well ? Both affect appetite regulation and energy expenditure.
Bottom Line
Your body requires roughly ??2100 kcal/day at rest (BMR) and about ??2600?2700 kcal/day when you factor in your typical activity level.
Start with that estimate, monitor progress, then adjust by small increments until you reach the desired results.
[2025-10-01 17:36:52.848952]
URL