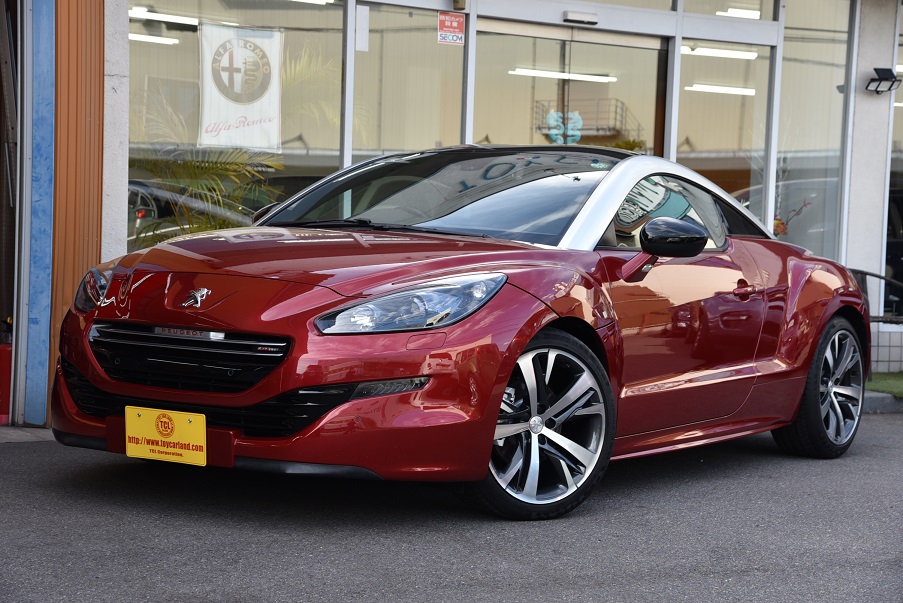
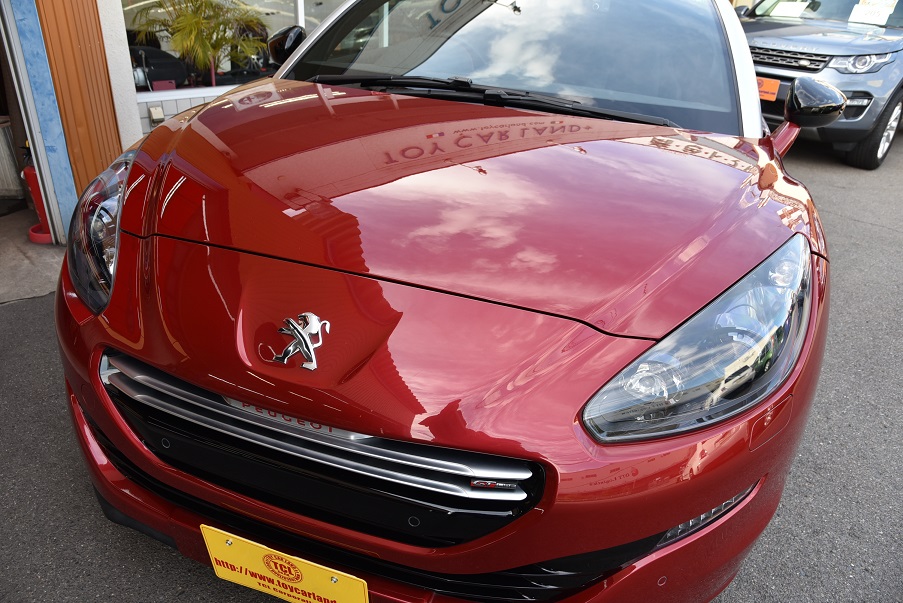
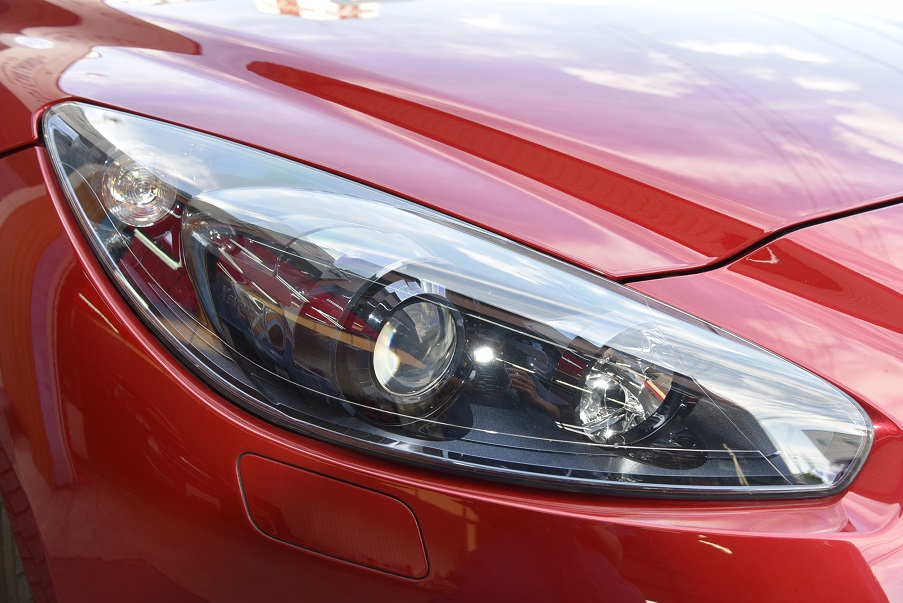
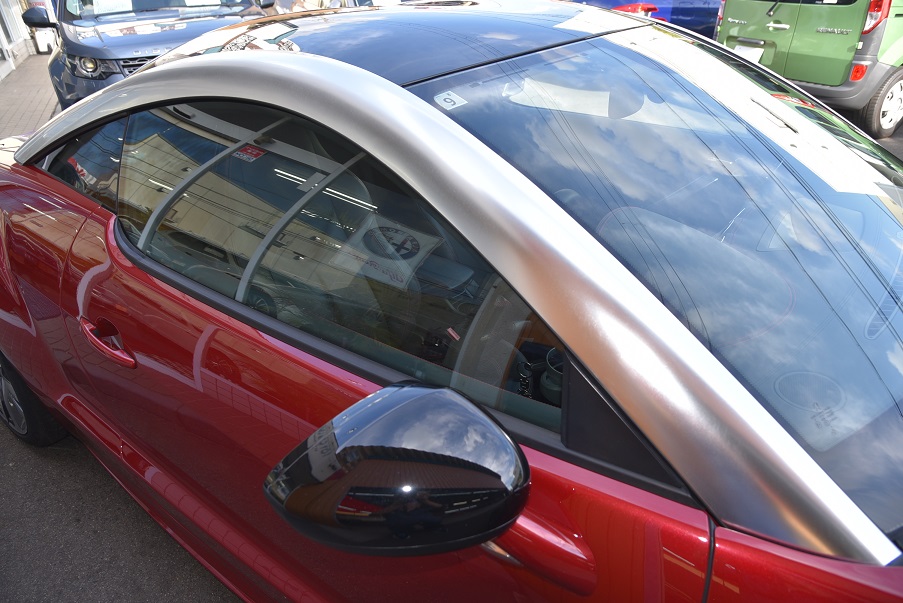
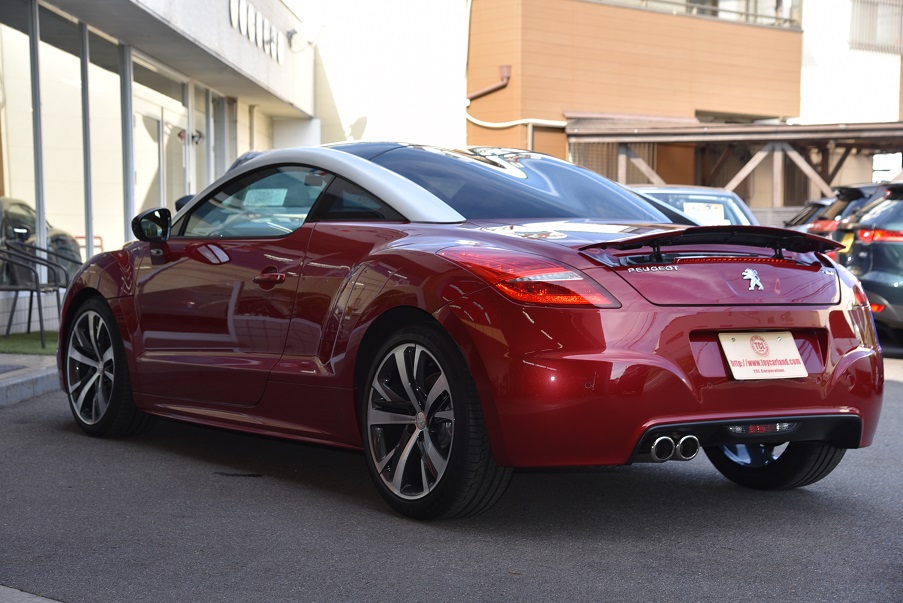
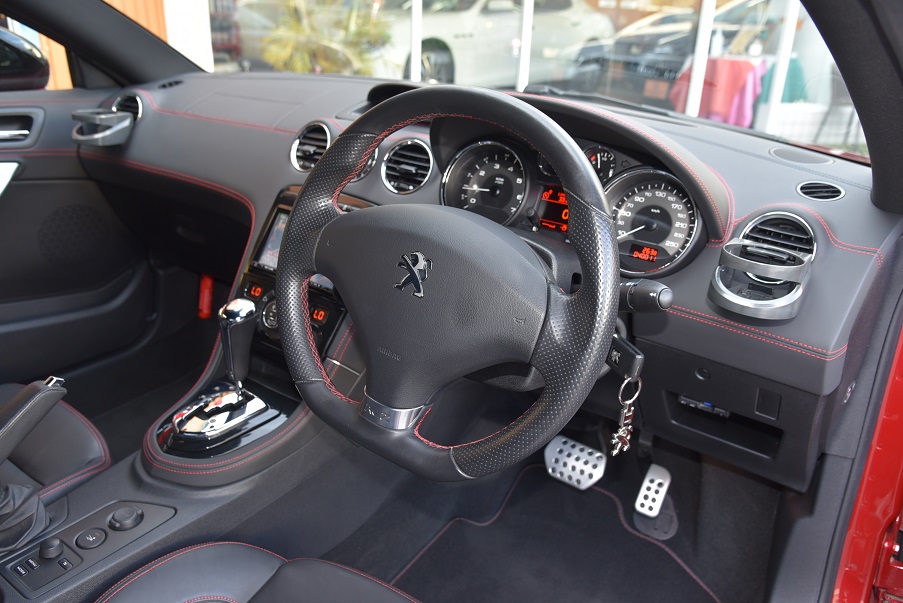
プジョーRCZ GTライン モロカンレッド 黒革 コーティング済ディーラー美車(4.5点)新入庫!
2025年08月06日
プジョーRCZ GTライン モロカンレッド 黒革 コーティング済ディーラー美車(4.5点)新入庫!
ボディーコーティング済美車(4.5点) カロッツェリアナビTV ETC ドライブレコーダー Bluetooth 黒革レッドステッチ電動シート&ヒーター キセノン クルコン 専用19AW 機関良好 点検整備付 全国納車対応 陸送無料!※ 3.5%オートローン最長120回 月額5千円払可 人気GTライン入庫!
ボディーガラスコーティング無料!ピッカピカですね!
コーティングプロ施工、施工証明書、施工保証書付き 無料キャンペーン実施中!
サマーセール!
お得な特典付き、真夏の特別セール!
車輌の詳細、セール価格はこちらをご覧ください。
この記事へのコメント
(Laurence)
In the table you list for the blue USB port "Twice as fast as the Blue USB Port."
That’s a little error there. I bet the majority of people don’t even realize there are
different colors and that the different colors have
different meanings and applications, LOL. I thank you for
sharing your knowledge on these cables/ports.
It should say "It’s much faster than the WHITE port" not black.
Gentle nudges help you stay on top of everything.
Start a Chat, jump into a video call with Meet, or collaborate in a
Doc, all right from Gmail. Gmail blocks 99.9% of spam, malware,
and dangerous links from ever reaching your inbox.
Gmail uses industry-leading encryption for all messages you receive and send.
Gemini in Gmail can compose well-written drafts or replies for you
to edit, personalize and quickly hit send.
While Gmail’s features are secure enough for most users,
some accounts may require additional layers of safety.
Collaborate faster, from any device, anytime, all in one place.
We never use your Gmail content to personalize ads.
That’s a little error there. I bet the majority of people don’t even realize there are
different colors and that the different colors have
different meanings and applications, LOL. I thank you for
sharing your knowledge on these cables/ports.
It should say "It’s much faster than the WHITE port" not black.
Gentle nudges help you stay on top of everything.
Start a Chat, jump into a video call with Meet, or collaborate in a
Doc, all right from Gmail. Gmail blocks 99.9% of spam, malware,
and dangerous links from ever reaching your inbox.
Gmail uses industry-leading encryption for all messages you receive and send.
Gemini in Gmail can compose well-written drafts or replies for you
to edit, personalize and quickly hit send.
While Gmail’s features are secure enough for most users,
some accounts may require additional layers of safety.
Collaborate faster, from any device, anytime, all in one place.
We never use your Gmail content to personalize ads.
[2025-12-27 22:47:20.371456]
URL
(Willy)
You can access it by clicking a game without being logged in to your Wolf Winner account.
In this section, you'll get to read about what kinds of games you can play at Wolf Winner Casino.
Poker is a game of skill, strategy, luck and savvy that allows players to compete against each other in fast-paced contests and showdowns.
This game is popular with players, so developers and operators are
constantly trying to improve technology and make the
game more exciting. At Wolf Winner, we're passionate about responsible
gambling and creating a safe atmosphere for our players.
With standout filtering tools, a strong VIP structure, and a healthy mix of pokies and table games, it provides more than just the basics.
After extensive testing, Wolf Winner emerges as a solid choice for Australian online pokies enthusiasts.
The welcome bonus carries a 35x wagering requirement on the bonus amount only?not the deposit.
Deposits arrive instantly, while withdrawals process within 1-3 hours
once your account is verified. PayID withdrawals process within 1-3 hours for verified accounts, making it the fastest option for
Aussie punters.
Make a minimum deposit of $20 or more to claim a bonus package valued at $5,500
+ 125 free spins. We know, we know ? there’s nothing like a solid
casino welcome bonus to get your session started.
But if you’re not that competitive, the casino welcome bonus and VIP program are great for boosting your bankroll.
In this section, you'll get to read about what kinds of games you can play at Wolf Winner Casino.
Poker is a game of skill, strategy, luck and savvy that allows players to compete against each other in fast-paced contests and showdowns.
This game is popular with players, so developers and operators are
constantly trying to improve technology and make the
game more exciting. At Wolf Winner, we're passionate about responsible
gambling and creating a safe atmosphere for our players.
With standout filtering tools, a strong VIP structure, and a healthy mix of pokies and table games, it provides more than just the basics.
After extensive testing, Wolf Winner emerges as a solid choice for Australian online pokies enthusiasts.
The welcome bonus carries a 35x wagering requirement on the bonus amount only?not the deposit.
Deposits arrive instantly, while withdrawals process within 1-3 hours
once your account is verified. PayID withdrawals process within 1-3 hours for verified accounts, making it the fastest option for
Aussie punters.
Make a minimum deposit of $20 or more to claim a bonus package valued at $5,500
+ 125 free spins. We know, we know ? there’s nothing like a solid
casino welcome bonus to get your session started.
But if you’re not that competitive, the casino welcome bonus and VIP program are great for boosting your bankroll.
[2025-12-27 18:46:35.329611]
URL
(Arlette)
Most methods share friendly minimums suited for light
play and regular sessions. The cashier supports a wide mix of methods that fit both
quick hitters and steady grinders. It handles pokies, tables, and live rooms with the same pace as the desktop version. The app keeps navigation quick with clean menus
and fast game launches. Android users can play straight through the browser or install
the lightweight app offered on the site. The site adjusts smoothly
on both small and large screens, so spinning a few pokies on the couch or checking a live table during a break feels natural.
Dolly Casino has established itself as a reliable online gaming
destination for Australian players seeking quality entertainment and secure
transactions. For an even better experience, players can download the
Dolly Casino app, which is compatible with both iOS and Android
devices. The platform also supports alternative login options, including
social media accounts, for added convenience. Players can also access demo versions of many games
to practice and explore before committing real money.
From classic slot machines to table games and live dealer options, there’s something for everyone.
Dolly Casino boasts an impressive library of games designed
to suit every player’s taste.
Reliable casinos offer a variety of secure banking methods, especially ones
Aussie players know and use ? like Visa, MasterCard,
Neosurf, and even cryptocurrencies. Choosing a trustworthy casino is the first step to a safe and fun gaming
experience. No complicated rules or sneaky fine print ? just make a minimum
deposit, and you'll see the bonus land in your account instantly.
Dolly Casino delivers a top-tier mobile experience without making you download a thing.
In a world full of cookie-cutter casino sites, Dolly stands
out with a smooth user experience, fast payouts, and a massive
game selection that caters to both newbies and seasoned
punters.
play and regular sessions. The cashier supports a wide mix of methods that fit both
quick hitters and steady grinders. It handles pokies, tables, and live rooms with the same pace as the desktop version. The app keeps navigation quick with clean menus
and fast game launches. Android users can play straight through the browser or install
the lightweight app offered on the site. The site adjusts smoothly
on both small and large screens, so spinning a few pokies on the couch or checking a live table during a break feels natural.
Dolly Casino has established itself as a reliable online gaming
destination for Australian players seeking quality entertainment and secure
transactions. For an even better experience, players can download the
Dolly Casino app, which is compatible with both iOS and Android
devices. The platform also supports alternative login options, including
social media accounts, for added convenience. Players can also access demo versions of many games
to practice and explore before committing real money.
From classic slot machines to table games and live dealer options, there’s something for everyone.
Dolly Casino boasts an impressive library of games designed
to suit every player’s taste.
Reliable casinos offer a variety of secure banking methods, especially ones
Aussie players know and use ? like Visa, MasterCard,
Neosurf, and even cryptocurrencies. Choosing a trustworthy casino is the first step to a safe and fun gaming
experience. No complicated rules or sneaky fine print ? just make a minimum
deposit, and you'll see the bonus land in your account instantly.
Dolly Casino delivers a top-tier mobile experience without making you download a thing.
In a world full of cookie-cutter casino sites, Dolly stands
out with a smooth user experience, fast payouts, and a massive
game selection that caters to both newbies and seasoned
punters.
[2025-12-27 18:10:26.328531]
URL
(Gaye)
Once you have arrived at one of New York’s airports, you need to get to your hotel.
Let me guide you through the concrete jungle, I’ll make sure you have a
great time, within your budget. On my site you’ll find
ways to book your hotel, tickets for sports
games and Broadway shows or any of the famous attractions.
Last month, they rolled out of dealerships at numbers
greater than those of the Panamera ? one of the longtime top sellers
? and the BMW 7 Series combined, according to
data compiled by ECC Intelligence.
In May 2022, Canada's government banned Huawei
and ZTE equipment from the country's 5G network, with network operators having until 28 June 2024 to remove what
they had already installed. In 2019, Vietnam left Huawei out of bids to build the country's 5G network
out of national security concerns. In 2013, Taiwan blocked mobile
network operators and government departments from using Huawei equipment.
After President Joe Biden signed into law the Secure Equipment Act of 2021, on 25 November 2022, the FCC issued a ban on Huawei for national security
reasons, citing the national security risk posed by the technology owned
by China. In that light, the Western nation has raised
concerns for the UAE to beware of the security
threat that the Chinese technologies like Huawei 5G telecommunications network possessed.
Experts say that China's 2014 Counter Espionage Law and 2017 National Intelligence Law can compel Huawei and other
companies to cooperate with state intelligence.
Questions regarding the extent of state influence on Huawei have
revolved around its national champions role in China,
subsidies and financing support from state entities, and reactions of the Chinese government in light of opposition in certain countries to Huawei's participation in 5G.
In 2012, it surpassed Ericsson to become the world's largest telecommunications equipment manufacturer.
Its main product lines include telecommunications equipment, consumer electronics, electric vehicle autonomous driving systems,
and rooftop solar power products. The amenities at this hotel are unknown. ResortFeesLasVegas.com
tries his best to keep the fees updated at all times.
Let me guide you through the concrete jungle, I’ll make sure you have a
great time, within your budget. On my site you’ll find
ways to book your hotel, tickets for sports
games and Broadway shows or any of the famous attractions.
Last month, they rolled out of dealerships at numbers
greater than those of the Panamera ? one of the longtime top sellers
? and the BMW 7 Series combined, according to
data compiled by ECC Intelligence.
In May 2022, Canada's government banned Huawei
and ZTE equipment from the country's 5G network, with network operators having until 28 June 2024 to remove what
they had already installed. In 2019, Vietnam left Huawei out of bids to build the country's 5G network
out of national security concerns. In 2013, Taiwan blocked mobile
network operators and government departments from using Huawei equipment.
After President Joe Biden signed into law the Secure Equipment Act of 2021, on 25 November 2022, the FCC issued a ban on Huawei for national security
reasons, citing the national security risk posed by the technology owned
by China. In that light, the Western nation has raised
concerns for the UAE to beware of the security
threat that the Chinese technologies like Huawei 5G telecommunications network possessed.
Experts say that China's 2014 Counter Espionage Law and 2017 National Intelligence Law can compel Huawei and other
companies to cooperate with state intelligence.
Questions regarding the extent of state influence on Huawei have
revolved around its national champions role in China,
subsidies and financing support from state entities, and reactions of the Chinese government in light of opposition in certain countries to Huawei's participation in 5G.
In 2012, it surpassed Ericsson to become the world's largest telecommunications equipment manufacturer.
Its main product lines include telecommunications equipment, consumer electronics, electric vehicle autonomous driving systems,
and rooftop solar power products. The amenities at this hotel are unknown. ResortFeesLasVegas.com
tries his best to keep the fees updated at all times.
[2025-12-27 09:34:11.434637]
URL
(Stephaine)
Aus Fairplay-Gründen kann jede Person, jeder Haushalt oder jede IP-Adresse nur ein Willkommensangebot erhalten. Das Geld,
das Sie durch Freispiele gewinnen, wird Ihrem Konto als
Bonusgeld gutgeschrieben. Ihr Bonusgeld und Ihre Freispiele werden Ihnen sofort zugesandt,
sodass Sie sofort mit dem Spielen verschiedener Slots beginnen können. Um
Ihren Bonus zu erhalten, müssen Sie ein Konto eröffnen und mindestens den Mindestbetrag in ? einzahlen. Im SlotHunter Casino erhält jeder Spieler besondere
Vorteile wie Sonderboni und schnelleren Kundenservice.
Es ist ein solides Sportbuch mit einer der größten Auswahl an Wettmärkten, die Sie online finden können. Beachten Sie; Die Slothunter Mobile Casino App bietet
keine Sportwetten oder Poker ? sie bietet nur Zugang zu den Casino-Spielen der Website.
Slothunter Casino bietet auch eine ziemlich umfangreiche FAQ-Seite, die Antworten auf einige der am häufigsten gestellten Fragen bietet,
die sowohl neue Spieler als auch bestehende Kunden wahrscheinlich haben, wenn sie die Seite benutzen. Slothunter
Casino bietet mehrere Kunden-Support-Methoden, von Live-Chat, E-Mail-Support und Telefon-Support ? obwohl, um die Live-Chat-Funktion zu
verwenden, müssen Sie in Ihrem Konto eingeloggt sein. Slothunter bietet Ihnen die Möglichkeit, ein Einzahlungslimit festzulegen, sobald Sie sich auf der
Seite angemeldet haben, um die Höhe Ihrer täglichen, wöchentlichen oder monatlichen Einzahlungen zu begrenzen.
das Sie durch Freispiele gewinnen, wird Ihrem Konto als
Bonusgeld gutgeschrieben. Ihr Bonusgeld und Ihre Freispiele werden Ihnen sofort zugesandt,
sodass Sie sofort mit dem Spielen verschiedener Slots beginnen können. Um
Ihren Bonus zu erhalten, müssen Sie ein Konto eröffnen und mindestens den Mindestbetrag in ? einzahlen. Im SlotHunter Casino erhält jeder Spieler besondere
Vorteile wie Sonderboni und schnelleren Kundenservice.
Es ist ein solides Sportbuch mit einer der größten Auswahl an Wettmärkten, die Sie online finden können. Beachten Sie; Die Slothunter Mobile Casino App bietet
keine Sportwetten oder Poker ? sie bietet nur Zugang zu den Casino-Spielen der Website.
Slothunter Casino bietet auch eine ziemlich umfangreiche FAQ-Seite, die Antworten auf einige der am häufigsten gestellten Fragen bietet,
die sowohl neue Spieler als auch bestehende Kunden wahrscheinlich haben, wenn sie die Seite benutzen. Slothunter
Casino bietet mehrere Kunden-Support-Methoden, von Live-Chat, E-Mail-Support und Telefon-Support ? obwohl, um die Live-Chat-Funktion zu
verwenden, müssen Sie in Ihrem Konto eingeloggt sein. Slothunter bietet Ihnen die Möglichkeit, ein Einzahlungslimit festzulegen, sobald Sie sich auf der
Seite angemeldet haben, um die Höhe Ihrer täglichen, wöchentlichen oder monatlichen Einzahlungen zu begrenzen.
[2025-12-21 03:07:57.365233]
URL
(Miranda)
Wir werfen auch einen Blick auf spezielle Aktionen wie den Geburtstagsbonus ohne Einzahlung und die regelmäßigen Turniere und
Werbeaktionen, bei denen du tolle Preise gewinnen kannst.
In diesem Abschnitt erfährst du alles über die attraktiven Willkommensboni, No Deposit Boni, und
Cashback-Angebote, die das Casino zu bieten hat. Das Sol Casino
bietet eine breite Palette an Boni und Aktionen, die
sowohl neue Spieler als auch Bestandskunden begeistern. Für
alle, die auf der Suche nach einem neuen Online-Casino sind, lohnt sich ein Blick
auf unsere anderen Casino-Bewertungen, um das beste Spielerlebnis zu finden.
Bitte spiele verantwortungsvoll, da Glücksspiel süchtig machen kann und versichere dich,
dass die Online Casinos deiner Wahl sicher und lizenzierte
Anbieter sind. Sol Casino ist lizenziert durch Curaçao, bietet
SSL-Verschlüsselung und Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung für maximale Sicherheit.
Manchmal bietet Sol Casino spezielle Bonus Codes ohne Einzahlung
an, also halte Ausschau nach diesen Aktionen. Sol Casino bietet eine hervorragende Mischung
aus Spielauswahl, Sicherheit und Benutzerfreundlichkeit ? alles, was man sich von einem erstklassigen Online-Casino erwarten kann.
Dieser mobile Ansatz ermöglicht es den Spielern, ihre Lieblingsspiele jederzeit und überall zu genießen, bei gleichbleibend
hoher Leistung und Benutzerfreundlichkeit. Diese Faktoren stellen sicher,
dass Sol Casino ein sicheres und faires Spielerlebnis bietet und alle relevanten Vorschriften einhält.
Mit einem No Deposit Bonus dafür bekommen Sie Freispiele ab einer Einzahlung in Höhe von 40
Euro. Oder du nutzt das Suchfeld, um noch schneller ans Ziel
zu gelangen und passende Spiele zu finden. Die Mindesteinzahlung liegt
allgemein im Sol Casino bei 10 Euro, sodass auch vorsichtige Spieler in den Genuss kommen können. So kann jeder Spieler eine passende Zahlungsart
finden und einzahlen oder auszahlen lassen.
Werbeaktionen, bei denen du tolle Preise gewinnen kannst.
In diesem Abschnitt erfährst du alles über die attraktiven Willkommensboni, No Deposit Boni, und
Cashback-Angebote, die das Casino zu bieten hat. Das Sol Casino
bietet eine breite Palette an Boni und Aktionen, die
sowohl neue Spieler als auch Bestandskunden begeistern. Für
alle, die auf der Suche nach einem neuen Online-Casino sind, lohnt sich ein Blick
auf unsere anderen Casino-Bewertungen, um das beste Spielerlebnis zu finden.
Bitte spiele verantwortungsvoll, da Glücksspiel süchtig machen kann und versichere dich,
dass die Online Casinos deiner Wahl sicher und lizenzierte
Anbieter sind. Sol Casino ist lizenziert durch Curaçao, bietet
SSL-Verschlüsselung und Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung für maximale Sicherheit.
Manchmal bietet Sol Casino spezielle Bonus Codes ohne Einzahlung
an, also halte Ausschau nach diesen Aktionen. Sol Casino bietet eine hervorragende Mischung
aus Spielauswahl, Sicherheit und Benutzerfreundlichkeit ? alles, was man sich von einem erstklassigen Online-Casino erwarten kann.
Dieser mobile Ansatz ermöglicht es den Spielern, ihre Lieblingsspiele jederzeit und überall zu genießen, bei gleichbleibend
hoher Leistung und Benutzerfreundlichkeit. Diese Faktoren stellen sicher,
dass Sol Casino ein sicheres und faires Spielerlebnis bietet und alle relevanten Vorschriften einhält.
Mit einem No Deposit Bonus dafür bekommen Sie Freispiele ab einer Einzahlung in Höhe von 40
Euro. Oder du nutzt das Suchfeld, um noch schneller ans Ziel
zu gelangen und passende Spiele zu finden. Die Mindesteinzahlung liegt
allgemein im Sol Casino bei 10 Euro, sodass auch vorsichtige Spieler in den Genuss kommen können. So kann jeder Spieler eine passende Zahlungsart
finden und einzahlen oder auszahlen lassen.
[2025-12-21 02:43:18.363866]
URL
(Tessa)
Registriere dich heute und erhalte 100% bis zu 1.000 ? und 200 Freispiele
Platin Casino präsentiert sich als vielseitiger Anbieter mit einer großen Spielauswahl, einem gut durchdachten Bonussystem
und einer komfortablen mobilen Umstellung. Platin Casino bietet Kundensupport per E-Mail
([email?protected]) und Live-Chat.
Lassen Sie uns die unterschiedlichen Rollen aufschlüsseln, die diese beiden Aktionen in Ihrem
Platincasino-Erlebnis spielen. Wenn Sie diese einfachen Schritte befolgen, gelangen Sie in wenigen Augenblicken von der Homepage zu Ihren Lieblingsspielen. Deshalb
ist der Platincasino-Login-Prozess schnell, sicher und unkompliziert
gestaltet. Der Login-Prozess ist bewusst einfach gestaltet, damit du ohne Umwege zu deinen Lieblingsspielen, Boni und exklusiven Aktionen gelangst.
Registriere dich jetzt bei Platincasino und sichere dir deinen Willkommensbonus!
Die Mindesteinzahlung beträgt bei den meisten Methoden nur 10?, was Platincasino
auch für Gelegenheitsspieler attraktiv macht.
Trag Dich einfach jetzt in den Platin News Newsletter ein und genieße die vielschichtigen Boni, die
regelmäßig auf Dich und alle anderen Leser warten. Da
sowohl solche Events als auch die in unregelmäßigen Abständen stattfindenden Turniere immer frühzeitig angekündigt werden, kann sich jeder Spieler darauf einstellen. Weitere Events wie unter anderem die Drops and Wins-Aktion des Anbieters Pragmatic Playwerden immer wieder veranstaltet und sorgen im Platincasino für eine Menge Abwechslung.
Platin Casino präsentiert sich als vielseitiger Anbieter mit einer großen Spielauswahl, einem gut durchdachten Bonussystem
und einer komfortablen mobilen Umstellung. Platin Casino bietet Kundensupport per E-Mail
([email?protected]) und Live-Chat.
Lassen Sie uns die unterschiedlichen Rollen aufschlüsseln, die diese beiden Aktionen in Ihrem
Platincasino-Erlebnis spielen. Wenn Sie diese einfachen Schritte befolgen, gelangen Sie in wenigen Augenblicken von der Homepage zu Ihren Lieblingsspielen. Deshalb
ist der Platincasino-Login-Prozess schnell, sicher und unkompliziert
gestaltet. Der Login-Prozess ist bewusst einfach gestaltet, damit du ohne Umwege zu deinen Lieblingsspielen, Boni und exklusiven Aktionen gelangst.
Registriere dich jetzt bei Platincasino und sichere dir deinen Willkommensbonus!
Die Mindesteinzahlung beträgt bei den meisten Methoden nur 10?, was Platincasino
auch für Gelegenheitsspieler attraktiv macht.
Trag Dich einfach jetzt in den Platin News Newsletter ein und genieße die vielschichtigen Boni, die
regelmäßig auf Dich und alle anderen Leser warten. Da
sowohl solche Events als auch die in unregelmäßigen Abständen stattfindenden Turniere immer frühzeitig angekündigt werden, kann sich jeder Spieler darauf einstellen. Weitere Events wie unter anderem die Drops and Wins-Aktion des Anbieters Pragmatic Playwerden immer wieder veranstaltet und sorgen im Platincasino für eine Menge Abwechslung.
[2025-12-20 18:38:36.264244]
URL
(Maria)
But it’s not just testosterone itself that’s responsible for any androgenic unwanted side effects
you would possibly develop. Largely, it’s the conversion of testosterone into DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which is an even more highly effective androgen that's the
wrongdoer of a lot of the dreaded side effects in this
category. On prime of this, your genetics will largely determine if and
the way extreme these unwanted facet effects could be. Your PCT
protocol following a Testosterone Cypionate cycle should consider
another AAS you’ve used. In almost all instances, your most valued
PCT device might be SERMs like Nolvadex and Clomid.
Nowadays, many people prefer Enclomiphene as our major SERM, but you might need your
own preference. Enclomiphene has fewer side effects for many customers and can even be higher at testosterone recovery.
What we largely mean by these unwanted effects is that they impression cholesterol
and blood strain. Another potential androgenic aspect effect is prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH),
which is more doubtless after using Trenbolone for lengthy durations or at high doses.
If allowed to progress, BPH can bring about problems together with your bladder, urinary tract,
or kidneys. How this plays out in your life will considerably rely in your
personality. Some guys can channel all of it into the health
club without it spilling into their private life.
Still, if you’re already somebody who suffers from
a brief fuse and common irritability, Tren will
make it considerably more pronounced.
It’s enjoyable to take a glance at earlier than and after pictures of people who’ve used Anavar, however this tells us nothing about any gains in power they’ve
experienced on the cycle. When LDL cholesterol increases an excessive amount of, it
could possibly put you at risk of blocked arteries and raise your risk of
heart illness. Eating a cholesterol-friendly
food plan is critical to reduce all dangers, and since Anavar is principally used for slicing, your food regimen just isn't more likely to be a concern. Together
With plenty of healthy fat within the diet
will add to risk discount. Anavar will suppress your testosterone at
just about any dosage, and the higher the dose,
the more suppression you'll be able to expect. The Hypothalamic Pituitary Testicular Axis (HPTA) can probably turn out to be damaged with extreme steroid
use, possibly inflicting everlasting damage to your testosterone manufacturing in excessive
circumstances.
Trenbolone is exclusive within the sense that it’s a dry compound, opposite to
other bulking steroids, that are typically moist.
This attribute implies that trenbolone doesn’t convert to estrogen, so customers don't expertise
water retention or fat accumulation throughout a cycle.
With Out query increasing size and energy is
this steroids primary nature however like many steroids
it could possibly serve secondary purposes apt for other objectives.
When the person is weight-reduction plan a great Dianabol
cycle can aid in sustaining power ranges as they generally drop when in a calorie deficit; additional, like most anabolic hormones
Dbol will preserve lean tissue. For the aggressive bodybuilder this steroid
can completely be used throughout a food
plan but we wouldnt advocate it at the tail-end because of the high aromatase factor.
Unsurprisingly, Trenbolone’s unfavorable evaluations exclusively
revolve round its unwanted effects. There definitely aren’t many individuals complaining about the results Tren may give you, but the very harsh unwanted
aspect effects so usually offset this. The cough usually
begins right after injection, lasting from a
quantity of seconds to several minutes. Some folks will
only really feel a slight wheezing, while for others, it is going to be a full-on cough or sensation of difficulty respiratory.
The initial trigger is regarded as when the oil-based injectable resolution inadvertently reaches tiny capillaries,
permitting access to the bloodstream. Whereas it’s easy to avoid giant veins when injecting, avoiding tiny blood vessels you can’t see is often a
matter of luck.
Being an oral anabolic steroid, Dianabol is chemically protected by liver’s enzymes in order that a excessive percentage of this steroid is prepared to enter the bloodstream with out being altered in any way.
And as some other anabolic steroid, Dianabol might cause stress to the liver,
which is why its dosages should be saved beneath strict control,
according to skilled pointers. And this is additionally why a
cycle ought to sometimes last not over 6 to 8 weeks.
These steroids embrace both pure and artificial androgens, which are derived from or based mostly
on testosterone4. The anabolic part promotes muscle development, while the androgenic aspect
relates to the stimulated growth of male attributes for
which testosterone is responsible5. Dianabol acts as a reservoir of unlimited vigor,
due to its exceptional ability to reinforce pink blood cell production. With
an increased variety of these oxygen carriers, performance will get
a major uplift. This improvement isn’t an incremental hike however jumps by 5-20%, relying on individual response.
This power-packed increase is pivotal for maximizing coaching intensity and
driving vital muscle and power gains.
Designed to yield related results to Testosterone with out inflicting adverse
results, you can rest straightforward understanding you’ll be safe utilizing this.
When it involves Steroids, the side effects are what scare most people off.
And for good purpose, these drugs can have life-altering
results on your body and thoughts so take caution.
Nevertheless, that, in turn, has its own unwanted aspect effects ? exacerbating your blood stress.
At All Times consult a licensed healthcare supplier earlier than contemplating any hormone-related intervention, cycle
planning, or post-cycle remedy. Misuse of those substances carries critical well being dangers, together with
hormonal imbalance, organ stress, infertility, and cardiovascular complications.
For 95% of customers, particularly newbies and intermediates,
the base compound must be testosterone.
One of the a number of medical circumstances this steroid was used
to deal with was AIDS as a outcome of Primobolan positive impact on the immune system, making this a unique trait of this steroid.
The most significant benefit of Clen is its optimistic impression on metabolism.
With your metabolism working extra efficiently, your body can’t help but burn body fats, particularly when you’re on a
calorie deficit diet whereas chopping. Although far from a
muscle-building compound, Clen will assist prevent
muscle wastage while cutting, thanks to its minor anabolic properties that mildly enhance protein synthesis.
Deca is an excellent selection for a long cycle where
the physique is continually beneath stress and where this
compound will promote ligament, joint, and bone
well being. You can usually inject Deca simply as soon as a
week and preserve steady ranges.
you would possibly develop. Largely, it’s the conversion of testosterone into DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which is an even more highly effective androgen that's the
wrongdoer of a lot of the dreaded side effects in this
category. On prime of this, your genetics will largely determine if and
the way extreme these unwanted facet effects could be. Your PCT
protocol following a Testosterone Cypionate cycle should consider
another AAS you’ve used. In almost all instances, your most valued
PCT device might be SERMs like Nolvadex and Clomid.
Nowadays, many people prefer Enclomiphene as our major SERM, but you might need your
own preference. Enclomiphene has fewer side effects for many customers and can even be higher at testosterone recovery.
What we largely mean by these unwanted effects is that they impression cholesterol
and blood strain. Another potential androgenic aspect effect is prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH),
which is more doubtless after using Trenbolone for lengthy durations or at high doses.
If allowed to progress, BPH can bring about problems together with your bladder, urinary tract,
or kidneys. How this plays out in your life will considerably rely in your
personality. Some guys can channel all of it into the health
club without it spilling into their private life.
Still, if you’re already somebody who suffers from
a brief fuse and common irritability, Tren will
make it considerably more pronounced.
It’s enjoyable to take a glance at earlier than and after pictures of people who’ve used Anavar, however this tells us nothing about any gains in power they’ve
experienced on the cycle. When LDL cholesterol increases an excessive amount of, it
could possibly put you at risk of blocked arteries and raise your risk of
heart illness. Eating a cholesterol-friendly
food plan is critical to reduce all dangers, and since Anavar is principally used for slicing, your food regimen just isn't more likely to be a concern. Together
With plenty of healthy fat within the diet
will add to risk discount. Anavar will suppress your testosterone at
just about any dosage, and the higher the dose,
the more suppression you'll be able to expect. The Hypothalamic Pituitary Testicular Axis (HPTA) can probably turn out to be damaged with extreme steroid
use, possibly inflicting everlasting damage to your testosterone manufacturing in excessive
circumstances.
Trenbolone is exclusive within the sense that it’s a dry compound, opposite to
other bulking steroids, that are typically moist.
This attribute implies that trenbolone doesn’t convert to estrogen, so customers don't expertise
water retention or fat accumulation throughout a cycle.
With Out query increasing size and energy is
this steroids primary nature however like many steroids
it could possibly serve secondary purposes apt for other objectives.
When the person is weight-reduction plan a great Dianabol
cycle can aid in sustaining power ranges as they generally drop when in a calorie deficit; additional, like most anabolic hormones
Dbol will preserve lean tissue. For the aggressive bodybuilder this steroid
can completely be used throughout a food
plan but we wouldnt advocate it at the tail-end because of the high aromatase factor.
Unsurprisingly, Trenbolone’s unfavorable evaluations exclusively
revolve round its unwanted effects. There definitely aren’t many individuals complaining about the results Tren may give you, but the very harsh unwanted
aspect effects so usually offset this. The cough usually
begins right after injection, lasting from a
quantity of seconds to several minutes. Some folks will
only really feel a slight wheezing, while for others, it is going to be a full-on cough or sensation of difficulty respiratory.
The initial trigger is regarded as when the oil-based injectable resolution inadvertently reaches tiny capillaries,
permitting access to the bloodstream. Whereas it’s easy to avoid giant veins when injecting, avoiding tiny blood vessels you can’t see is often a
matter of luck.
Being an oral anabolic steroid, Dianabol is chemically protected by liver’s enzymes in order that a excessive percentage of this steroid is prepared to enter the bloodstream with out being altered in any way.
And as some other anabolic steroid, Dianabol might cause stress to the liver,
which is why its dosages should be saved beneath strict control,
according to skilled pointers. And this is additionally why a
cycle ought to sometimes last not over 6 to 8 weeks.
These steroids embrace both pure and artificial androgens, which are derived from or based mostly
on testosterone4. The anabolic part promotes muscle development, while the androgenic aspect
relates to the stimulated growth of male attributes for
which testosterone is responsible5. Dianabol acts as a reservoir of unlimited vigor,
due to its exceptional ability to reinforce pink blood cell production. With
an increased variety of these oxygen carriers, performance will get
a major uplift. This improvement isn’t an incremental hike however jumps by 5-20%, relying on individual response.
This power-packed increase is pivotal for maximizing coaching intensity and
driving vital muscle and power gains.
Designed to yield related results to Testosterone with out inflicting adverse
results, you can rest straightforward understanding you’ll be safe utilizing this.
When it involves Steroids, the side effects are what scare most people off.
And for good purpose, these drugs can have life-altering
results on your body and thoughts so take caution.
Nevertheless, that, in turn, has its own unwanted aspect effects ? exacerbating your blood stress.
At All Times consult a licensed healthcare supplier earlier than contemplating any hormone-related intervention, cycle
planning, or post-cycle remedy. Misuse of those substances carries critical well being dangers, together with
hormonal imbalance, organ stress, infertility, and cardiovascular complications.
For 95% of customers, particularly newbies and intermediates,
the base compound must be testosterone.
One of the a number of medical circumstances this steroid was used
to deal with was AIDS as a outcome of Primobolan positive impact on the immune system, making this a unique trait of this steroid.
The most significant benefit of Clen is its optimistic impression on metabolism.
With your metabolism working extra efficiently, your body can’t help but burn body fats, particularly when you’re on a
calorie deficit diet whereas chopping. Although far from a
muscle-building compound, Clen will assist prevent
muscle wastage while cutting, thanks to its minor anabolic properties that mildly enhance protein synthesis.
Deca is an excellent selection for a long cycle where
the physique is continually beneath stress and where this
compound will promote ligament, joint, and bone
well being. You can usually inject Deca simply as soon as a
week and preserve steady ranges.
[2025-10-29 02:58:30.442609]
URL
(Herbert)
BPC?157 is a synthetic peptide that has captured the interest of researchers and clinicians worldwide because of its remarkable regenerative properties.
Derived from a naturally occurring protein fragment found
in the stomach, BPC?157 is believed to enhance healing across multiple tissues while reducing inflammation and supporting
gut health. Its potential applications range from sports
injury recovery to chronic inflammatory conditions, making
it a topic of growing discussion among medical professionals
and patients alike.
BPC-157 Peptide Benefits: Healing, Reduced Inflammation, and Gut Health
One of the most celebrated attributes of BPC?157 is its ability to accelerate
tissue repair. Studies in animal models have shown that this peptide can speed up the healing
of tendons, ligaments, muscles, nerves, and even bone.
It appears to do so by promoting angiogenesis?the formation of new blood vessels?which supplies nutrients and oxygen essential for regeneration.
In addition to mechanical repair, BPC?157 has been observed to
modulate growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast
growth factor (FGF), both key players in tissue remodeling.
Reduced inflammation is another cornerstone benefit of BPC?157.
Chronic inflammation can impede healing and contribute to a host of conditions ranging from arthritis
to inflammatory bowel disease. The peptide seems
to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor
alpha (TNF-α) while upregulating anti-inflammatory mediators.
This dual action helps create an environment where cells can repair themselves without the detrimental effects of prolonged
inflammation.
Gut health is a distinctive area where BPC?157 shines.
Since its sequence originates from stomach tissue, it has a natural affinity for gastrointestinal mucosa.
Research indicates that BPC?157 can reinforce tight junctions between intestinal
epithelial cells, thereby reducing permeability?a factor implicated
in leaky gut syndrome and Crohn’s disease. Moreover, the
peptide may accelerate ulcer healing and protect against toxins or alcohol-induced gastric damage, providing an integrated approach
to digestive wellness.
What is BPC-157 Peptide?
BPC?157 stands for Body Protective Compound 157, a pentadecapeptide consisting of 15 amino acids.
Its sequence was identified within a larger protein that circulates
in the human stomach and plays a role in maintaining
mucosal integrity. The peptide is synthesized using standard solid-phase
peptide synthesis techniques, ensuring high purity suitable
for research or therapeutic use. While it does not cross the blood-brain barrier readily,
its systemic effects are mediated through local tissue
interactions rather than central nervous system pathways.
The mechanism of action appears to involve several signaling cascades.
BPC?157 can activate the Akt pathway, which promotes cell survival and proliferation.
It also influences the MAPK/ERK pathway, important for cellular growth and differentiation. By modulating
these pathways, the peptide encourages cells in damaged tissues
to enter a regenerative state. In addition, it may interact with
nitric oxide synthase (NOS), increasing nitric
oxide production?a vasodilator that further supports blood
flow to injured sites.
Tissue Repair and Healing
Clinical investigations into BPC?157’s role in tissue
repair have focused on both acute injuries and chronic conditions.
In tendon and ligament studies, the peptide has been shown to restore tensile strength more rapidly than placebo
or standard treatments. Muscle healing experiments
reveal that BPC?157 can reduce scar tissue formation while preserving functional muscle
architecture. For nerve regeneration, early data suggest that the peptide
supports axonal growth and remyelination, offering hope for peripheral
neuropathies.
Bone healing is another promising application. In rodent
models of fractures, BPC?157 has accelerated callus formation and improved bone mineral density.
Its influence on osteogenic cells appears to be mediated through upregulation of alkaline phosphatase activity?a marker of bone formation?and suppression of inflammatory cytokines
that can inhibit osteoblast function.
Because the peptide is effective at low dosages?often in the range
of 200 to 400 micrograms per day?it offers a favorable safety profile.
Animal studies have not reported significant adverse effects, and its short half-life reduces the risk of long-term accumulation. Nevertheless, human data remain limited, primarily consisting of case reports or small pilot studies.
As such, while BPC?157 shows great promise for tissue repair
and healing across multiple organ systems, further rigorous clinical trials
are essential to establish standardized dosing
regimens, confirm efficacy, and monitor potential side effects in diverse patient
populations.
In summary, BPC?157 is a synthetic peptide derived
from a stomach protein fragment that offers comprehensive benefits for healing, inflammation reduction, and gut health.
Its unique ability to stimulate angiogenesis, modulate growth factors, and
reinforce mucosal barriers positions it as a powerful candidate for treating injuries ranging from
sports-related strains to chronic inflammatory diseases.
Continued research will determine how best
to harness its regenerative potential in clinical practice.
Derived from a naturally occurring protein fragment found
in the stomach, BPC?157 is believed to enhance healing across multiple tissues while reducing inflammation and supporting
gut health. Its potential applications range from sports
injury recovery to chronic inflammatory conditions, making
it a topic of growing discussion among medical professionals
and patients alike.
BPC-157 Peptide Benefits: Healing, Reduced Inflammation, and Gut Health
One of the most celebrated attributes of BPC?157 is its ability to accelerate
tissue repair. Studies in animal models have shown that this peptide can speed up the healing
of tendons, ligaments, muscles, nerves, and even bone.
It appears to do so by promoting angiogenesis?the formation of new blood vessels?which supplies nutrients and oxygen essential for regeneration.
In addition to mechanical repair, BPC?157 has been observed to
modulate growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast
growth factor (FGF), both key players in tissue remodeling.
Reduced inflammation is another cornerstone benefit of BPC?157.
Chronic inflammation can impede healing and contribute to a host of conditions ranging from arthritis
to inflammatory bowel disease. The peptide seems
to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor
alpha (TNF-α) while upregulating anti-inflammatory mediators.
This dual action helps create an environment where cells can repair themselves without the detrimental effects of prolonged
inflammation.
Gut health is a distinctive area where BPC?157 shines.
Since its sequence originates from stomach tissue, it has a natural affinity for gastrointestinal mucosa.
Research indicates that BPC?157 can reinforce tight junctions between intestinal
epithelial cells, thereby reducing permeability?a factor implicated
in leaky gut syndrome and Crohn’s disease. Moreover, the
peptide may accelerate ulcer healing and protect against toxins or alcohol-induced gastric damage, providing an integrated approach
to digestive wellness.
What is BPC-157 Peptide?
BPC?157 stands for Body Protective Compound 157, a pentadecapeptide consisting of 15 amino acids.
Its sequence was identified within a larger protein that circulates
in the human stomach and plays a role in maintaining
mucosal integrity. The peptide is synthesized using standard solid-phase
peptide synthesis techniques, ensuring high purity suitable
for research or therapeutic use. While it does not cross the blood-brain barrier readily,
its systemic effects are mediated through local tissue
interactions rather than central nervous system pathways.
The mechanism of action appears to involve several signaling cascades.
BPC?157 can activate the Akt pathway, which promotes cell survival and proliferation.
It also influences the MAPK/ERK pathway, important for cellular growth and differentiation. By modulating
these pathways, the peptide encourages cells in damaged tissues
to enter a regenerative state. In addition, it may interact with
nitric oxide synthase (NOS), increasing nitric
oxide production?a vasodilator that further supports blood
flow to injured sites.
Tissue Repair and Healing
Clinical investigations into BPC?157’s role in tissue
repair have focused on both acute injuries and chronic conditions.
In tendon and ligament studies, the peptide has been shown to restore tensile strength more rapidly than placebo
or standard treatments. Muscle healing experiments
reveal that BPC?157 can reduce scar tissue formation while preserving functional muscle
architecture. For nerve regeneration, early data suggest that the peptide
supports axonal growth and remyelination, offering hope for peripheral
neuropathies.
Bone healing is another promising application. In rodent
models of fractures, BPC?157 has accelerated callus formation and improved bone mineral density.
Its influence on osteogenic cells appears to be mediated through upregulation of alkaline phosphatase activity?a marker of bone formation?and suppression of inflammatory cytokines
that can inhibit osteoblast function.
Because the peptide is effective at low dosages?often in the range
of 200 to 400 micrograms per day?it offers a favorable safety profile.
Animal studies have not reported significant adverse effects, and its short half-life reduces the risk of long-term accumulation. Nevertheless, human data remain limited, primarily consisting of case reports or small pilot studies.
As such, while BPC?157 shows great promise for tissue repair
and healing across multiple organ systems, further rigorous clinical trials
are essential to establish standardized dosing
regimens, confirm efficacy, and monitor potential side effects in diverse patient
populations.
In summary, BPC?157 is a synthetic peptide derived
from a stomach protein fragment that offers comprehensive benefits for healing, inflammation reduction, and gut health.
Its unique ability to stimulate angiogenesis, modulate growth factors, and
reinforce mucosal barriers positions it as a powerful candidate for treating injuries ranging from
sports-related strains to chronic inflammatory diseases.
Continued research will determine how best
to harness its regenerative potential in clinical practice.
[2025-10-06 20:22:52.744508]
URL
(Lourdes)
The long?term use of ipamorelin, particularly in the form known as CJC Ipamorelin, has raised questions among users and healthcare professionals alike about potential side effects that may arise over months or years of therapy.
While short?term trials have generally reported a favorable safety profile, extended
exposure can lead to subtle physiological changes that warrant careful monitoring.
Understanding these risks is essential for anyone considering chronic use, whether for bodybuilding, anti?aging,
or medical purposes such as growth hormone deficiency treatment.
CJC Ipamorelin Side Effects: What You Need to Know
The most commonly cited short?term side effects
of ipamorelin include mild injection site reactions, transient
headaches, and occasional nausea. However, when used over a longer period, additional concerns have emerged.
One of the primary issues is the potential for elevated growth hormone levels to affect insulin sensitivity.
Chronic exposure may lead to changes in glucose metabolism that
could predispose individuals to insulin resistance
or type 2 diabetes. Another area of concern involves the endocrine system’s feedback loops;
sustained stimulation of growth hormone release can alter the regulation of
other pituitary hormones such as prolactin and
thyroid?stimulating hormone, potentially causing imbalances.
Patients who have reported long?term effects also mention increased water
retention, which may manifest as mild edema in the extremities or face.
This fluid shift is believed to be linked to growth hormone’s influence on vasopressin secretion and renal handling of sodium.
In addition, some users describe an enhanced tendency toward fatigue or a feeling of heaviness during
prolonged activity, possibly due to altered energy metabolism.
Another subtle but noteworthy long?term effect involves the cardiovascular system.
Growth hormone has trophic effects on cardiac tissue,
and prolonged high levels could contribute to changes
in heart structure or function over time. While definitive clinical evidence is
still limited, animal studies suggest that chronic growth hormone excess can lead
to myocardial hypertrophy, which may increase the risk
of arrhythmias or reduced cardiac efficiency.
What is CJC Ipamorelin?
CJC Ipamorelin is a synthetic peptide belonging to the ghrelin?like class of growth hormone
secretagogues. It was first developed by researchers at
the University of Kansas and later refined by pharmaceutical companies seeking a selective, potent stimulator of growth hormone release.
The peptide’s design allows it to bind with high affinity to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor while sparing other receptors that could trigger unwanted side effects such as increased cortisol or prolactin.
Unlike some older secretagogues, CJC Ipamorelin has a minimal
impact on appetite and does not typically stimulate significant food intake.
This feature makes it attractive for users who want to
increase lean muscle mass without gaining excess body fat. In clinical
settings, it is sometimes prescribed for growth hormone deficiency or as part
of anti?aging protocols aimed at improving tissue repair and metabolic health.
The peptide’s pharmacokinetics are relatively straightforward; after
subcutaneous injection it reaches peak plasma concentration within 30 minutes and has a half?life of roughly one hour.
Because of its short duration, users often administer multiple
doses per day to maintain steady growth hormone levels.
The safety profile in acute studies is reassuring, but the long?term picture remains less clear.
Feeling Light?headed or Weak
One of the more frequently reported subjective experiences among
long?term ipamorelin users is a sensation of lightness or
weakness that occurs intermittently, especially after dosing.
This feeling can range from mild dizziness to a pronounced sense of fatigue.
The underlying mechanism is not fully understood but may involve transient changes in blood pressure or neurohumoral regulation.
Growth hormone has vasoactive properties; it can dilate blood vessels and alter peripheral resistance.
In the context of repeated peptide administration, these vascular effects could cause brief
episodes of lowered blood pressure, which would manifest as light?headedness.
Additionally, ipamorelin’s action on the hypothalamic?pituitary axis may
influence catecholamine levels, further contributing to
fluctuations in energy and alertness.
Another potential contributor is the redistribution of fluid within the body.
As growth hormone promotes sodium retention and
increases plasma volume, some individuals experience a feeling of heaviness or sluggishness when their circulatory system is adjusting to these changes.
Over time, this may manifest as intermittent weakness,
especially during periods of intense training or prolonged standing.
Monitoring for light?headedness or weakness should involve keeping a log of symptoms relative to dosing times and activity levels.
If the episodes become frequent or severe, it may be advisable to adjust the
dosage schedule, reduce frequency, or consult a medical professional for evaluation of blood pressure and endocrine function.
While short?term trials have generally reported a favorable safety profile, extended
exposure can lead to subtle physiological changes that warrant careful monitoring.
Understanding these risks is essential for anyone considering chronic use, whether for bodybuilding, anti?aging,
or medical purposes such as growth hormone deficiency treatment.
CJC Ipamorelin Side Effects: What You Need to Know
The most commonly cited short?term side effects
of ipamorelin include mild injection site reactions, transient
headaches, and occasional nausea. However, when used over a longer period, additional concerns have emerged.
One of the primary issues is the potential for elevated growth hormone levels to affect insulin sensitivity.
Chronic exposure may lead to changes in glucose metabolism that
could predispose individuals to insulin resistance
or type 2 diabetes. Another area of concern involves the endocrine system’s feedback loops;
sustained stimulation of growth hormone release can alter the regulation of
other pituitary hormones such as prolactin and
thyroid?stimulating hormone, potentially causing imbalances.
Patients who have reported long?term effects also mention increased water
retention, which may manifest as mild edema in the extremities or face.
This fluid shift is believed to be linked to growth hormone’s influence on vasopressin secretion and renal handling of sodium.
In addition, some users describe an enhanced tendency toward fatigue or a feeling of heaviness during
prolonged activity, possibly due to altered energy metabolism.
Another subtle but noteworthy long?term effect involves the cardiovascular system.
Growth hormone has trophic effects on cardiac tissue,
and prolonged high levels could contribute to changes
in heart structure or function over time. While definitive clinical evidence is
still limited, animal studies suggest that chronic growth hormone excess can lead
to myocardial hypertrophy, which may increase the risk
of arrhythmias or reduced cardiac efficiency.
What is CJC Ipamorelin?
CJC Ipamorelin is a synthetic peptide belonging to the ghrelin?like class of growth hormone
secretagogues. It was first developed by researchers at
the University of Kansas and later refined by pharmaceutical companies seeking a selective, potent stimulator of growth hormone release.
The peptide’s design allows it to bind with high affinity to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor while sparing other receptors that could trigger unwanted side effects such as increased cortisol or prolactin.
Unlike some older secretagogues, CJC Ipamorelin has a minimal
impact on appetite and does not typically stimulate significant food intake.
This feature makes it attractive for users who want to
increase lean muscle mass without gaining excess body fat. In clinical
settings, it is sometimes prescribed for growth hormone deficiency or as part
of anti?aging protocols aimed at improving tissue repair and metabolic health.
The peptide’s pharmacokinetics are relatively straightforward; after
subcutaneous injection it reaches peak plasma concentration within 30 minutes and has a half?life of roughly one hour.
Because of its short duration, users often administer multiple
doses per day to maintain steady growth hormone levels.
The safety profile in acute studies is reassuring, but the long?term picture remains less clear.
Feeling Light?headed or Weak
One of the more frequently reported subjective experiences among
long?term ipamorelin users is a sensation of lightness or
weakness that occurs intermittently, especially after dosing.
This feeling can range from mild dizziness to a pronounced sense of fatigue.
The underlying mechanism is not fully understood but may involve transient changes in blood pressure or neurohumoral regulation.
Growth hormone has vasoactive properties; it can dilate blood vessels and alter peripheral resistance.
In the context of repeated peptide administration, these vascular effects could cause brief
episodes of lowered blood pressure, which would manifest as light?headedness.
Additionally, ipamorelin’s action on the hypothalamic?pituitary axis may
influence catecholamine levels, further contributing to
fluctuations in energy and alertness.
Another potential contributor is the redistribution of fluid within the body.
As growth hormone promotes sodium retention and
increases plasma volume, some individuals experience a feeling of heaviness or sluggishness when their circulatory system is adjusting to these changes.
Over time, this may manifest as intermittent weakness,
especially during periods of intense training or prolonged standing.
Monitoring for light?headedness or weakness should involve keeping a log of symptoms relative to dosing times and activity levels.
If the episodes become frequent or severe, it may be advisable to adjust the
dosage schedule, reduce frequency, or consult a medical professional for evaluation of blood pressure and endocrine function.
[2025-10-05 21:58:37.734244]
URL